SECaaS -Providing security through a service The risk of experiencing a loss of information security, data, and financial value is steadily increasing at a rapid pace. Meanwhile, this is being recognized, handled, and reduced concurrently. Numerous unreported cyberattacks remain undiscovered by businesses, with some still mysterious. Today, we will initiate a conversation concerning the significance of AI, cybersecurity, and the role of security as a service in our present-day world.
Before we delve further into security intelligence or SECaaS, let’s gain a clear understanding of the terminology used in this context. Kindly take note that the entire conversation will revolve around the FinTech sector since that is my area of expertise.
Emerging Technologies – AI, ML and DL
As per Sir Andrew NG, AI is the new electricity to power up any business of today, with the ability to kill the business if ignored. Machine learning and deep learning are subdomains of the AI domain.

- Artificial Intelligence – “Security as a Service,” with Artificial Intelligence emerges as a pivotal force, providing a robust framework for innovative solutions. Serving as a comprehensive canopy, AI’s heuristic methodologies, encompassing both explicit and meta-heuristic approaches, drive the evolution of security paradigms. By leveraging advanced algorithms and data analytics, AI empowers the development of dynamic security protocols, ensuring resilience and adaptability across diverse technological landscapes. In this capacity, AI serves as a cornerstone for safeguarding digital ecosystems, fostering continual innovation, and enhancing the efficacy of security-as-a-service offerings.”
- Machine Learning – Here, computer algorithms autonomously learn from vast datasets and information, enhancing the proactive detection and mitigation of security threats. It signifies the convergence of business acumen with cutting-edge technology, where the synergy between security expertise and emerging advancements fuels collaborative innovation. As a cornerstone of security strategy, Machine Learning empowers proactive threat detection and response, elevating the effectiveness and resilience of security-as-a-service offerings.
- Deep Learning – A subset of machine learning, holds significant relevance within the realm of Security as a Service. It represents an algorithmic approach devoid of theoretical constraints, capable of continually enhancing its capabilities with increased data input and computational resources. As a foundational component of security frameworks, Deep Learning transcends traditional limitations, enabling the analysis of vast datasets to identify complex patterns and anomalies, thus bolstering the efficacy of security-as-a-service solutions.
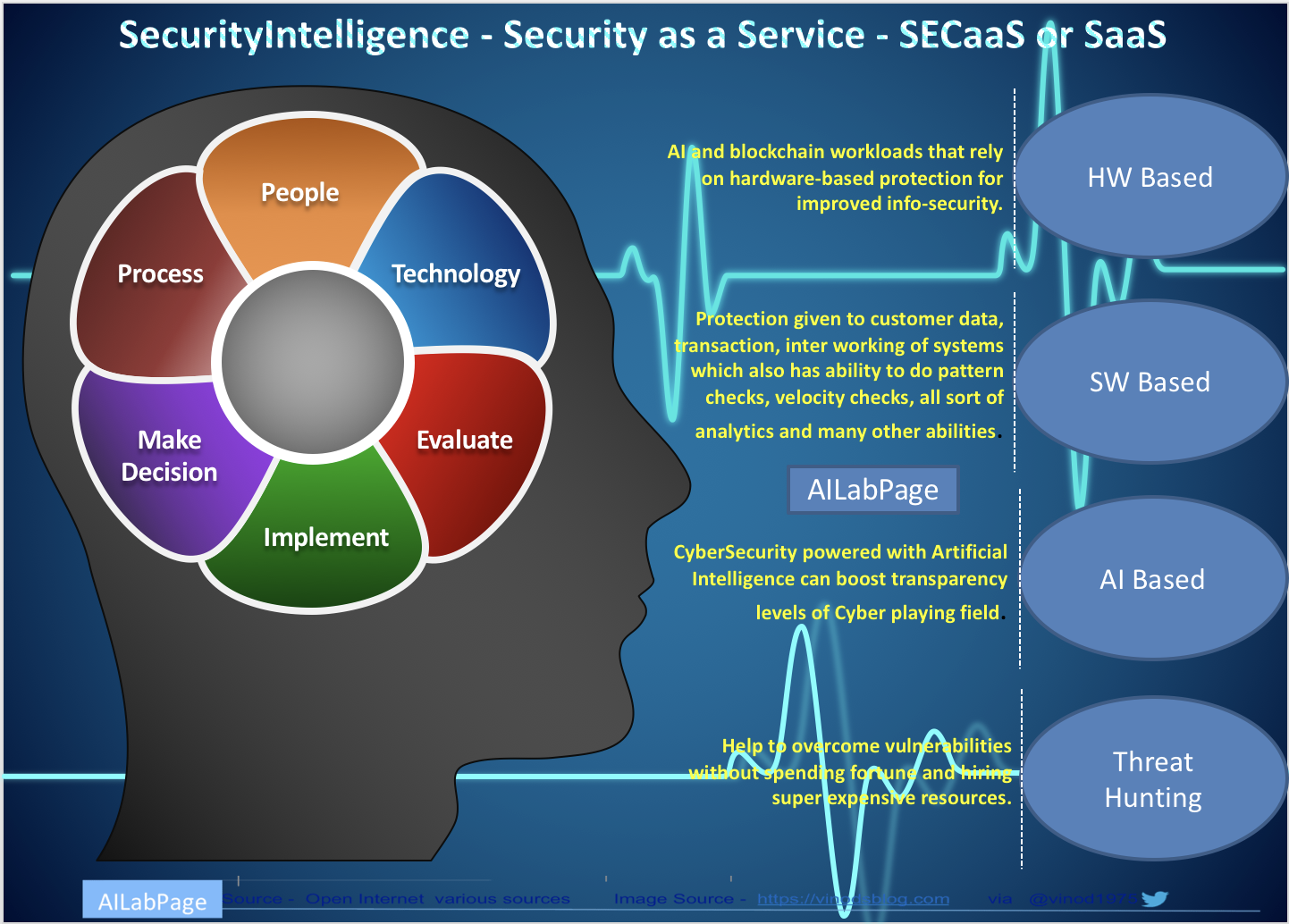
Software-Based Security
In modern and emerging markets, “software-based security,” or info-security,” is the protection given to customer data, transactions, and the interworking of systems, which also has the ability to do pattern checks, velocity checks, all sorts of analytics, and many other abilities. A few modes of digital payment
- Banking Cards (Credit, Debit, Stored Value, Prepaid): Used with PoS machines, ATMs, and Online
- Instant Payments: authenticates the identity of the user, like a debit card, using the phone as a tool instead of a separate card (smartphone and bank account).
- Digital wallets are a type of electronic card used for transactions made online through a computer or a smart phone. – The utility of an e-wallet is the same as a credit or debit card. Make paperless money transactions easier.
- Banking transaction out of the bank at PoS with the help of a banking correspondent.
- USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data): mobile banking for feature phones Security around USSD
- AirInterface Security: Between the handset and the nearest tower, UnSecure
- Core Network Security: Between Tower and USSDGW: Unsecure
- But both can be encrypted, and the reason it’s not done is because of the payload it puts on the network, which has no business case. Unfortunately, all USSD messages in the GSM network transfer as plain text. Having said all this, USSDGW is still far better because of the skill needed to hack. But after messages reach the server, they can be easily encrypted and hacked.
In the FinTech domain, information security secures electronic transactions and enables interoperability between applications across diverse platforms and operating systems. Authenticating cardholders and merchants, ensuring the confidentiality of information and payment data, defining protocols, and identifying electronic security service providers are a few areas where AI is outperforming.
Hardware-Based Security
AI and blockchain workloads that rely on hardware-based protection for improved information security AI is already “a thing” in security and crime prevention in many parts of the world today. Hardware boosting on per-chip throughput is given more priority and importance than just becoming a unit on the scaling line.
Intel software guard extensions, or SGX, are a set of CPU instruction codes that enable and execute the selected code and data in protected areas called enclaves. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are applied and developed across this spectrum. The neural network model for detecting and predicting information security issues needs a large data set. Along with data, it also needs faster processors, boosted chips, FPGAs, GPUs, and similar technology. AI-based hardware for info-security inference can support the below segments of problems:
- Cyberattacks and software errors or failures
- Security and Crime Prevention
- Privacy Protection
- Differential Privacy:
- IoT Systems Security
- Analytics of Consumer Information
- Game Theory
Cyber security is improving as a result of the explosion of machine-learning software, but so are hackers. Software developers, hardware designers, and system designers are going back to school. Current challenges in computing power and storage requirements are pushing service and product providers to go back and look at boosting per-chip throughput and not scaling out platforms over warehouses of boxes.
Digital wallet software on top of AI-based hardware It secures cardholders’ online purchases via a point-and-click interface. With the public key used to sign communication that has a key entity in a cryptographic system,
Artificial Intelligence – The Super Hero of CyberSecurity
Cybersecurity powered by artificial intelligence can boost the transparency levels of the cyber playing field. The appeal of AI for cyber security has extremely good reasons, like automation of operational tasks, developing and delivering predictive capabilities, mitigating human biases, and deriving doable intelligence. On the downside, AI requires high volumes of high-quality data to learn. Data silos and varying formats can affect training.

Given the dynamic cyber landscape, use cases need to stand the test of time and context, but most of the time, this negates their value. AI in cybersecurity has some questions, as below.
- Will artificial intelligence take over cybersecurity?
- How will the next level of cybersecurity become an AI-powered, data-centric model?
- AI and cybersecurity: friends or foes?
Cybersecurity with artificial intelligence will get smarter at the same time as cybercrime. What’s the next stage in cybersecurity?
- Maybe a simple AI-powered, data-centric model with huge processing power.
- Analytical trends and patterns can be modelled with any velocity of data to make quick decisions, etc.
Data-centric models help eliminate noise and discard it for other uses. Motivations and applications of AI in cybersecurity have a huge list, so we will not be able to cover them all here. Begin your AI-filled cybersecurity journey now.
Security Intelligence – Security as a Service – SECaaS or SaaS
SECaaS is another business model of today, like MLaaS, AIaaS, BaaS, etc. In this model, service providers integrate their security services ecosystem into any business. In return, we charge a monthly subscription fee. This method of information security brings cost-effectiveness, transfer of ownership, and speed to corporations. SECaaS also has a shorter time to value than traditional security offerings.
- Threat intelligence simplifies and streamlines threat hunting processes, enhancing predictability and effectiveness.
- In FinTech, leveraging advanced AI and machine learning technologies for fraud hunting significantly reduces instances of fraud, functioning as a next-generation antivirus solution. This service, offered in an “as-a-service” model, proactively identifies potential frauds, including those introduced by malware, contributing to robust cybersecurity measures.
Adopting security-as-a-service also addresses the industry skills gap. AI and machine learning techniques, especially predictive analytics, can leverage anomaly detection to identify potential security threats. SECaaS service providers, or domain-specialized managed security service providers, do a much better job and help companies fill the gap for their limited time and resources.
Threat Intelligence and SECaaS
The right SECaaS provider always helps to overcome vulnerabilities without spending a fortune or hiring super expensive resources. This is possible with a brand new technique called “threat intelligence.” With this intelligence, it’s now possible to determine the difference between a bot and a human, and this intelligence allows the network to respond to the attack patterns without any form of interaction from the human interface.
- Utilization of threat intelligence enhances convenience and predictability in threat hunting processes.
- Fraud detection within the FinTech sector is simplified and made more accessible, leading to a notable reduction in fraudulent activities.
- Distinguishing between bot and human activity presents a significant breakthrough in cybersecurity intelligence, overcoming challenges associated with rapidly evolving tactics.
- Challenges faced by SECaaS service providers include concerns regarding data loss for service seekers, regulatory compliance violations, and the impact of DoS and DDoS attacks on service availability.
- Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of security-as-a-service offerings, ensuring comprehensive protection for service seekers.
- Most SECaaS providers integrate their services with service seekers existing infrastructure or deploy hybrid environments for use of a mix of cloud and on-premise resources.
The process of detecting fraudulent activities in the FinTech industry can be likened to cutting-edge antivirus software that is driven by advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning. This particular service has the capability to function as an “as-a-service” model in detecting possible fraudulent activities caused by malware infiltrating a computer system. Be cautious in your enthusiasm for cyber intelligence and SECaaS, as the implementation of AI in cybersecurity has both beneficial and potentially harmful consequences.
 Conclusion – SECaaS model gets distorted as applications software, storage, and infrastructure runs remotely. Cybersecurity is NOT just an information technology department. People in the same department does not own the problem or responsibility in full. It is the job of every employee and even customers of the organisation. As per google search engine, identities are being stolen online every 3 seconds 24/7. So what are we doing, how can we protect it? GDPR makes it even more relevant. There are organizations which has suffered the cyber attacks, about to suffer and may have suffered but don’t know. To find better answers on this we need AI techniques to get over this. Understanding the relationship between AI or science that can imitate human beings and Cybersecurity that is an essential need for all is the key to success in business today.
Conclusion – SECaaS model gets distorted as applications software, storage, and infrastructure runs remotely. Cybersecurity is NOT just an information technology department. People in the same department does not own the problem or responsibility in full. It is the job of every employee and even customers of the organisation. As per google search engine, identities are being stolen online every 3 seconds 24/7. So what are we doing, how can we protect it? GDPR makes it even more relevant. There are organizations which has suffered the cyber attacks, about to suffer and may have suffered but don’t know. To find better answers on this we need AI techniques to get over this. Understanding the relationship between AI or science that can imitate human beings and Cybersecurity that is an essential need for all is the key to success in business today.
—
Similar Posts
Books + Other readings Referred
- Open Internet – NewsPortals, Economic development report papers
- Personal & professional working experience of @AILabPage members.
Disclaimer
All credit and credits of contributions remain with original authors and I sincerely thanks for their contribution here. In this post, we have discussed the potential merger of AI and its bundle pack i.e. Machine Learning, data science and analytics. In the next post, we will pick up a specific use case to deliberate on.
Feedback & Further Question
Do you have any questions about CyberSecurity Intelligence where AI is an integral part of it? Leave a comment or ask your question in the comments section below or ask your question via email. Will try my best to answer it.
============================ About the Author =======================
Read about Author at : About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your opinion / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter ====================================================================

Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting.
Cybersecurity has never been more important. Cybercriminals are becoming more prevalent and more sophisticated every day. At the same time, penalties for data breaches and loss of sensitive data are getting more severe. Companies can no longer afford to ignore the need for serious, hard-hitting cybersecurity.
Thanks. I have a question for you.