Recursive Neural Networks (Rv NNs) – are like master puzzle-solvers for structured data. Imagine handing them a jumble of words or a messy family tree—they don’t just see individual pieces, but how everything fits together.

By applying the same set of weights recursively, they build meaning layer by layer, like stacking LEGO blocks into a coherent shape. Whether it’s parsing a sentence or analyzing molecular structures, RecNNs thrive on hierarchy, turning chaos into order one branch at a time.
What makes them special? Unlike traditional neural networks that plow through data in a straight line, RecNNs embrace the beautiful mess of tree-like relationships. Each parent node combines information from its children, using shared weight matrices to preserve context and connections. Think of it like a family reunion: the same genetic rules (weights) apply to every branch, but the outcomes—whether it’s Uncle Bob’s nose or your cousin’s wit—are wonderfully diverse. This adaptability makes them ace players in tasks like understanding language syntax or mapping protein folds, where structure is everything.
RecNNs demand careful tuning, and their complexity can make even seasoned AI engineers sweat. Yet, they’re worth the effort when you need to model relationships that aren’t just sequential but deeply nested (like decoding a sentence’s grammar or a 3D protein’s folds). After all, the world isn’t linear—why should our AI be?
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is an undeniably mind-blowing machine learning technique that teaches computers to do what comes naturally to humans: learn by example. It can be used easily to predict the unpredictable. Researchers and engineers are busy creating artificial intelligence by using a combination of non-bio-neural networks and natural intelligence.

Deep learning, in short, is going much beyond machine learning and its algorithms that are either supervised or unsupervised. DL uses many layers of nonlinear processing units for feature extraction and transformation. It has revolutionized today’s industries by demonstrating near-human-level accuracy in certain tasks. tasks like pattern recognition, image classification, voice or text decoding, and many more.
Deep Learning is a key technology
- To voice control in mobile devices like handphones, TVs, vice command enabled speakers and TVs
- Behind driverless cars, enabling them to recognise a stop sign or to distinguish a pedestrian from a lamppost.
- Has revolutionised, image processing & classification and also speech recognition with high accuracy.
Deep learning has been getting lots of attention lately, and for good reason. It is achieving results that were not possible before. Business leaders and the developer community absolutely need to understand what it is, what it can do, and how it works.
| Category | Key Concept | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | What is Deep Learning? | A subset of machine learning that uses advanced techniques to achieve superior results from the same dataset. |
| Foundation | Inspired by Natural Intelligence | Mimics the mechanics of biological neural systems (natural intelligence). |
| Complexity | Training Techniques | Uses complex methods like deep neural networks, making it more sophisticated than traditional ML. |
| Learning Approach | Representation Learning | Focuses on learning data representations rather than using task-specific algorithms, unlike other ML methods. |
| Key Technique | Problem Solving | Solves problems by deeply understanding underlying patterns in data instead of following explicit programming rules. |
| Current Trend | Representation-Centric Focus | The approach emphasizing learned data representations in artificial neural networks is widely adopted and considered cutting-edge in the field today. |
Hoping that there would be no time when we need to do the reverse i.e. where will use Artificial Intelligence to create Natural Intelligence in future. So in nutshell, we need to be careful not to translate any of our research or machine learning into human experiences.
What is Recursive Neural Networks?
Recursive neural networks are family members and a kind of deep neural network. They are generally created after applying the same set of weights recursively to the structured inputs. This happens at every node for the same reason. RNNS are comprised of a class of architecture that operates on structured inputs, particularly directed acyclic graphs.

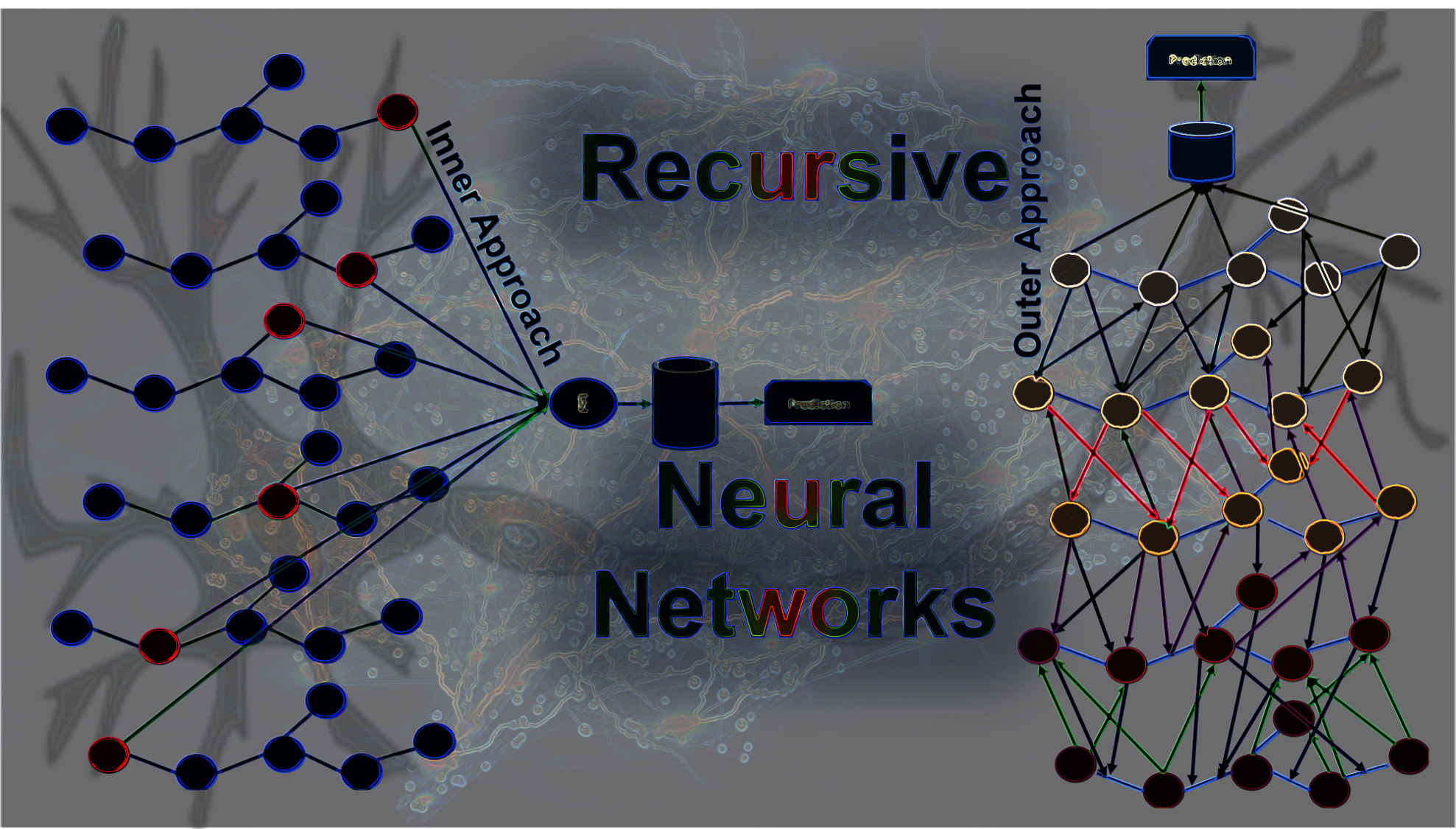
Recursive Neural Networks: Call it a deep tree-like structure. When the need is to parse a whole sentence, we use a recursive neural network. A tree-like topology allows branching connections and hierarchical structure. Arguments here can be made about how recursive neural networks are different from recurrent neural networks. We can simply divide recursive neural network approaches into two categories as shown below.
- Inner Approach – This approach usually conducts recursion inside the underlying graph and the objective is achieved usually by moving forward slowly around the edges of the graph.
- Outer Approach – This approach usually conducts recursion outside the underlying graph and aggregates information over progressively longer distances in a rectangular direction.
You know, the magic of Recursive Neural Networks (RvNNs) really comes alive when we look at how they explore structured data—almost like climbing through a tree, one branch at a time, in a thoughtful, top-down manner. What makes them truly special isn’t just the input they’re given, but also the context around it. They don’t just read a word and move on—they try to understand how that word fits into the bigger picture.
Understanding Structures Beyond Time
Now, here’s where it gets interesting: Recurrent neural networks are actually a very specific kind of recursive network. Picture a straight line, a timeline—step by step, moment by moment. That’s an RNN. It’s designed to make sense of sequences, like a sentence unfolding word by word or the beat of a song flowing from one note to the next. Each step is connected to the one before it, creating a continuous memory of sorts.
But a Recursive Neural Network doesn’t follow a timeline. Instead, it’s all about hierarchy. It looks at how elements nest inside each other—like how phrases make up a sentence, or how emotions build up through a paragraph. Think of it like climbing a family tree rather than following a linear path. So, in a nutshell:
🌱 Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) = Recursive networks arranged in a straight line over time.
🌳 Recursive Neural Networks (RvNNs) = Generalized, tree-structured models that capture relationships in nested, hierarchical data.

You’ll often see RvNNs shine in tasks like sentiment analysis. Let’s say someone writes, “I didn’t like the movie, although the soundtrack was beautiful.” A simple model might get confused by the word “beautiful”, but an RvNN understands that “didn’t like” governs the overall sentiment. It reads between the lines—literally.
- Questions – How recursive neural networks are different from recurrent neural networks?
- Answer – Recurrent neural networks are in fact recursive neural networks with a particular structure: that of a linear chain.
Originally, these networks were introduced because we needed a better way to grasp structured information—like logical expressions or nested phrases—where relationships between parts truly matter. That’s the beauty of it. Recursive models let us peel back the layers of language, emotion, and logic to see how everything fits together. It’s not just about classifying words—it’s about understanding the soul of a sentence.
Recurrent vs Recursive Neural Networks
Recurrent and recursive neural networks are two interchangeable terms that can be used to refer to the same thing. Most commonly, they are referred to using the identical abbreviation, RNN. Recursive networks can be understood as an expansion of recurrent networks, as both involve repetition over a period of time. Essentially, they share common characteristics.

| Aspect | Recursive Neural Networks (ReNNs) | Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical structure where parent nodes have children nodes similar to themselves, forming a hierarchical network. Example: Image segmentation, where each node represents a region of an image, and child nodes represent sub-regions. | Linear structure where neurons are connected in a sequence, allowing information to persist over time. Example: Text generation tasks like language modeling, where RNNs process input text word by word. |
| Processing Mechanism | Process input hierarchically, resembling a tree structure, without a time aspect to the input sequence. Example: Natural language processing tasks such as parsing sentences, where ReNNs analyze sentence structures. | Process input sequentially over time, allowing information to be retained and updated at each time step. Example: Time series forecasting, where RNNs predict future values based on past observations. |
| Handling of Hierarchical Structures | Effective at handling any hierarchical structure, combining representations of child nodes into parent representations. Example: Image recognition tasks, where ReNNs analyze hierarchical features like edges, shapes, and objects. | Less effective at capturing hierarchical relationships and may require additional mechanisms to handle hierarchical data. Example: Analyzing text documents with nested sections, where ReNNs may struggle to capture hierarchical relationships. |
| Temporal Aspect | Does not inherently capture temporal dependencies in data. | Captures temporal dependencies well, making them suitable for sequential data processing tasks. Example: Speech recognition, where RNNs analyze sequential audio frames to transcribe spoken words. |
| Applications | Suitable for tasks involving hierarchical relationships, such as parsing sentences, analyzing hierarchical data, and processing tree-like structures. Example: Language translation, where ReNNs process sentences hierarchically to capture grammatical structures. | Widely used in sequential data processing tasks, such as time series forecasting, natural language processing, and speech recognition. Example: Sentiment analysis, where RNNs process text sequentially to determine the sentiment of a sentence. |
As we now know, networks that operate on structured classes are more recursive. If we stack multiple recursive layers, then those can be called deep recursive neural networks. In a recurrent network, the weights are shared along the length of the sequence, though dimensionality remains constant. The answer to why this is the case is simply because it helps to deal with position-dependent weights when encountering a sequence at test time of different lengths at train time.
Principles of Recursive Neural Networks
Recurrent neural networks are, in fact, recursive neural networks. Because recursive networks are mainly inherently complex, they are not yet accepted broadly. They are quite expensive in the computational learning phase.

Usually, these results are produced by systematically applying a consistent set of weights to the arranged inputs in a repetitive manner. This occurrence happens consistently across all points due to identical causative elements.
- Recursive neural networks, akin to deep neural networks, are a modified variant within the same computational model family, demonstrating versatility in handling classification and regression tasks.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), on the other hand, constitute a distinct structured model tailored for directed acyclic graphs, specifically designed to manage sequentially arranged inputs.
- While recursive networks are adept at addressing various learning tasks, RNNs specialize in tasks involving temporal dependencies and sequential data due to their focused design for ordered input processing.
It depends on how the math of the algorithm was translated into instructions for the computer you are using. And it depends on how much time you have. To us at AILabPage, we say machine learning is a crystal-clear and simple task. It is not only for PhD aspirants; it’s for you, us, and everyone.

Conclusion – I particularly think that getting to know the types of machine learning algorithms helps to see a somewhat clear picture. The answer to the question “What machine learning algorithm should I use?” is always “It depends.” It depends on the size, quality, and nature of the data. Also, what is the data torturing’s objective or motivation? As we torture data, more useful information comes out. It depends on how the math of the algorithm was translated into instructions for the computer you are using. And it depends on how much time you have. To us at AILabPage, we say machine learning is a crystal clear and simple task. It is not only for PhD aspirants; it’s for you, us, and everyone.
—
Not Covered here
Topics we have not covered in this post but are extremely critical and important to understand to get a little more strong hands-on RNNs please find the links as below.
- Sequential Memory
- Backpropagation Algorithm Basics
- LSTM – Long Short-Term Memory Architecture and Mathematical Foundation of LSTM Networks
- GRU – Gated Recurrent Unit a Powerful Architecture
Points to Note:
All credits, if any, remain with the original contributor. We have covered all the basics of recursive neural networks. RNNs are all about modeling units in sequence. The perfect support for natural language processing (NLP) tasks Though often such tasks struggle to find the best companion between CNN and RNN algorithms to look for information,
Books + Other readings Referred
- Research through the open internet, news portals, white papers, and imparted knowledge via live conferences and lectures.
- Lab and hands-on experience of @AILabPage (Self-taught learners group) members.
- This useful pdf on NLP parsing with Recursive NN.
- Amazing information in this pdf as well.
======================= About the Author =======================
Read about Author at : About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your opinion / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter
============================================================

[…] Recursive Neural Networks […]
Thank you so much for sharing this amazing blog with us. Anyone who are searching for more, free training’s like Data science, Python, Java, Asp.Net, Nodejs and more programming languages please contact Nareshit.
NodeJS Online Training
Data Science Online Training
It was very informative.Thanks for sharing it.
I have some updates of Data Science.Please click on this link to know https://gomodulus.com/page/contact-us
[…] Recursive Neural Networks […]
[…] Neural Networks (RNNs), Recursive Neural Networks (ReNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) can be […]