Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning – Both supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms are foundational in the field of machine learning and have distinct purposes. From my hands-on experience in the lab at AILabPage, I’ve come to appreciate how these two approaches complement each other.

Supervised learning revolves around labeled data. The algorithm essentially learns from examples where both input and corresponding output are provided. It feels like guiding a trainee step-by-step, helping it map inputs to desired outputs through reverse engineering, unlike traditional programming where rules are predefined. For example, in one of my projects, we trained a supervised algorithm to identify architectural styles from labeled images of buildings. The precision of predictions was like having a smart assistant who could name each style just by looking at the design.
On the other hand, unsupervised learning is more exploratory. It dives into unlabeled data to uncover hidden patterns and structures. Working with unsupervised algorithms felt like peeling back the layers of a mystery—it doesn’t need explicit instructions but learns to cluster or associate data based on inherent similarities. In one experiment, I fed a dataset of untagged landscape photos into an unsupervised model, and it grouped them by features like mountains, waterfalls, and deserts. Watching it uncover patterns I hadn’t explicitly programmed was fascinating.
These two approaches embody different philosophies in machine learning. Where supervised learning relies on guidance and feedback, unsupervised learning thrives on curiosity and discovery. Their synergy, when combined thoughtfully, can unlock incredible insights.
Machine Learning – Introduction
AILabPage defines machine learning as “A focal point where business, data and experience meet emerging technology and decide to work together“. ML instructs an algorithm to learn for itself by analyzing data. Algorithms here learn a mapping of input to output, detection of patterns, or reward.

The more data it processes, the smarter the algorithm gets. Thanks to statistics, machine learning became very famous in the 1990s. Machine Learning is about the use and development of fancy learning algorithms. The intersection of computer science and statistics gave birth to probabilistic approaches in AI. You can follow the link below for more details on Machine Learning.
In other words, Machine learning algorithms “learn” from the observations. When exposed to more observations, the algorithm improves its predictive performance. Although ML is magnificent implementing this bundle pack of ML for practical use in businesses is still a hurdle for many.

ML’s current excellence can be explained by several reasons, such as those provided below although not exclusively.
- The explosion of big data
- Hunger for new business and revenue streams in this business shrinking times
- Advancements in machine learning algorithms
- Development of extremely powerful machine with high capacity & faster computing ability
- Storage capacity
As of today, sadly, most machine learning methods are based on supervised learning. Which means we still have a long way to go. In the Fintech domain, we say “machine learning” is the future (actually, that future is now) of “e-commerce,” and “data scientists” will work as batmen for “fintech” and “puretech.” Today’s machines are learning and performing tasks that were only done by humans in the past, like making better judgments and decisions, playing games, etc.
Understanding Supervised Learning
Supervised Machine Learning – Machine learning algorithms “learn” from the observations. When exposed to more observations, the algorithm improves its predictive performance. SML through a historic data set can hunt for correct answers, and the task of the algorithm is to find them in the new data. Supervised Machine Learning is
- Is a task of deducing function from labelled training data.
- Making predictions based on evidence in the presence of uncertainty
- Identifying patterns in given data with adaptive algorithms

Definition and Core Concepts
At its heart, supervised learning is about training algorithms using labeled data. Labeled data means that every input (feature) is paired with a corresponding output (label). The algorithm learns to identify patterns and relationships between these inputs and outputs to make predictions on new, unseen data.
Think of it as teaching someone to recognize architectural styles: you show them pictures of buildings (inputs) with their names (outputs). Over time, they learn to associate the features of each building with its style. Similarly, supervised learning algorithms predict outcomes based on the patterns they’ve learned during training. Key concepts include:
- Training Dataset: The dataset with labeled examples used to train the algorithm.
- Validation and Testing: Ensuring the model’s performance on data it hasn’t seen before.
- Generalization: The algorithm’s ability to make accurate predictions on new data.
How Supervised Learning Works: Labeled Data and Mapping Outputs
The process of supervised learning involves three primary steps:

- Training Phase: The algorithm is exposed to a dataset with labeled inputs and outputs. It analyzes the data to find relationships between the two.
- Learning Phase: Using optimization techniques, the algorithm adjusts its internal parameters to minimize errors in its predictions.
- Prediction Phase: Once trained, the model applies its learned patterns to make predictions on new, unseen data.
An example from my lab experience: I trained a model using labeled images of landscapes. Each image was tagged with specific features like “waterfall,” “mountain,” or “desert.” The algorithm learned to associate visual cues—like edges, textures, and colors—with these labels. Later, when given a new image, it could confidently classify it based on these learned patterns.

Real-Life Applications of Supervised Learning
Supervised learning shines in scenarios where clear, labeled data is available. Some of the most impactful applications include:
- Predicting Housing Prices:
Algorithms are trained on datasets with features like location, square footage, and number of rooms (inputs) paired with sale prices (outputs). Once trained, these models can predict the price of a house based on its features. - Image Classification:
Supervised learning plays a significant role in recognizing and categorizing images. For example, in architecture, models can be trained to classify buildings into styles like Gothic, Modern, or Baroque based on labeled datasets of images and style
Hands-On Example: Training a Model to Recognize Patterns in Landscape Photos
During one of my experiments at AILabPage, I worked on training a supervised learning model to classify landscape photos. Here’s how I approached it:
| Phase | Details | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset Preparation | – Collected a dataset of labeled images: waterfalls, mountains, forests, and deserts. – Ensured diversity by including images from different seasons and lighting conditions. | A well-balanced dataset that minimized bias and represented various landscapes effectively. |
| Training the Model | – Used a convolutional neural network (CNN) optimized for image data. – Monitored training to adjust parameters and prevent overfitting. | The model learned to identify features like edges, textures, and patterns unique to landscapes. |
| Testing and Validation | – Tested the model with unseen images to evaluate its generalization capability. | The model performed well, accurately categorizing unseen landscape photos. |
| Results | – Distinguished landscapes like misty mountains and cascading waterfalls with high precision. | Demonstrated the effectiveness of supervised learning in real-world applications. |
| Takeaway | – Highlighted the power of supervised learning and the importance of proper tools and techniques. | Reinforced the accessibility of AI for practical use cases in domains like photography. |
In short supervised learning is a fundamental approach in machine learning that feels like guiding a curious learner with clear examples and feedback. From my hands-on experience in the AILabPage, I’ve observed how this method transforms raw data into powerful predictive tools, enabling machines to understand the world in a structured and logical way.

Supervised learning, as I’ve experienced firsthand, is a robust and versatile method. It’s not just about building models—it’s about empowering machines to learn from our structured guidance, creating solutions that simplify and enrich our lives.
Understanding Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is like discovering the hidden stories within data. At AILabPage, my hands-on experience taught me how powerful this approach can be when we aim to uncover patterns and structures without predefined labels. It’s a journey of exploration where the algorithm acts as a detective, piecing together clues to form meaningful insights.

- A technique with the idea to explore hidden gems/patterns.
- To find some intrinsic structure in data.
- That something can’t be seen with the naked eye requires a magnifier (UML)
At its core, unsupervised learning transforms raw, unstructured data into something interpretable and actionable.
Definition and Core Concepts
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where the algorithm learns from unlabelled data. Unlike supervised learning, there’s no direct guidance or output to map the input data to. Instead, the goal is to identify underlying patterns, groupings, or structures within the data.
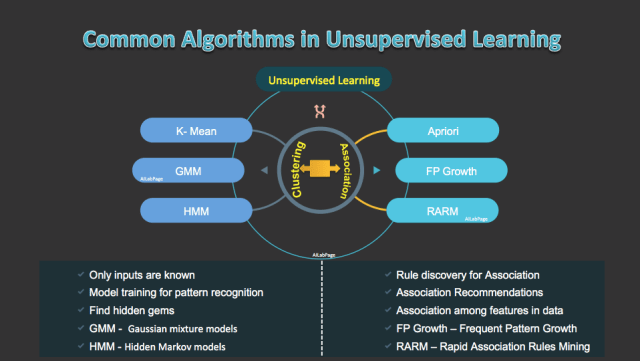
Key techniques in unsupervised learning include:
- Clustering: Grouping similar data points together based on shared characteristics.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Simplifying data while retaining its essential features.
Unsupervised Learning; is one of three types of machine learning i.e. Supervised Machine Learning, Unsupervised Machine Learning (UML) and Reinforcement Learning. The most common method in UML is cluster analysis. Cluster analysis is used for exploring hidden patterns or grouping data behind data analysis. The algorithm used in this is to draw inferences from data sets consisting of input data without labels.
How Unsupervised Learning Works: Hidden Patterns and Clustering
Unsupervised learning algorithms work by analyzing data to find hidden structures.

- Clustering: Algorithms like K-Means or DBSCAN group similar data points. For example, in landscape images, clustering might identify distinct groups such as waterfalls, mountains, or forests without prior labeling.
- Association: Algorithms detect relationships within data. For instance, finding commonalities in photography features like lighting, color, or texture.
Through mathematical models, these algorithms reveal patterns that might not be immediately apparent to humans, offering new ways to analyze and utilize data.
Real-Life Applications
- Customer Segmentation in Marketing
Marketers use clustering to divide customers into groups based on purchasing habits or demographics. This helps tailor personalized marketing strategies, increasing engagement and conversions. - Grouping Landscape Images by Natural Features
In photography, unsupervised learning can cluster images based on visual characteristics. For instance:- Images with similar textures (e.g., rocky mountains vs. flowing water).
- Color palettes (e.g., autumn leaves vs. snow-covered peaks).
This is invaluable when managing large photography collections or curating albums.
Hands-On Example: Analyzing Hidden Structures in Data
During one of my experiments at AILabPage, I applied unsupervised learning to analyze landscape photography data. Here’s how it unfolded.
| Step | Details | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset Creation | – Compiled a collection of unlabelled landscape images, covering mountains, waterfalls, and forests. | Diverse dataset ensured robust analysis, accounting for various natural and lighting conditions. |
| – Included diversity with different seasons, weather conditions, and lighting scenarios. | ||
| Clustering with K-Means | – Preprocessed images to extract features like edges, colors, and textures using computer vision techniques. | Images clustered into meaningful groups such as waterfalls, snowy peaks, and forests. |
| – Applied the K-Means algorithm to identify distinct groups in the dataset. | ||
| Observations and Insights | – Grouped images with similar natural features (e.g., snowy peaks together, lush forests in another group). | Discovered unique patterns like variations in waterfall flow intensity and light reflections. |
| – Identified sub-patterns that were otherwise hidden in the dataset. | ||
| Applications | – Streamlined photography organization by automatically creating thematic albums. | Improved efficiency in managing large photo collections. |
| – Enabled better planning for future shoots by analyzing feature trends (e.g., lighting preferences in waterfalls). | Enhanced strategic preparation for capturing landscapes effectively. |
Unsupervised learning is a powerful tool that thrives on the absence of labels. It’s a reminder that sometimes, the best insights come from exploring the unknown. Whether it’s grouping customers for better marketing or clustering landscape images for efficient organization, this approach unlocks new possibilities. My journey at AILabPage has shown me how unsupervised learning bridges the gap between raw data and actionable insights, making it a must-have tool in any data scientist’s arsenal.

Unsupervised learning – UML helps to find a hidden jewel in data by grouping similar things together. Data have no target attribute. The algorithm takes training examples as the set of attributes/features alone. In this post, I have summarised my whole upcoming book “Unsupervised Learning – The Unlabelled Data Treasure” on one page. This one-page guide is to know everything about unsupervised learning on a high level.
Key Differences Between Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
From my hands-on experiments at AILabPage, I’ve often navigated the nuanced differences between supervised and unsupervised learning. Both are integral pillars of machine learning, but their approaches, goals, and applications differ significantly. Here’s an inclusive and practical dive into these distinctions, rooted in real-world scenarios.

In short, supervised learning thrives on labeled data for precise predictions, while unsupervised learning uncovers hidden patterns in raw data. Understanding when to apply each is key to building intelligent, adaptive AI systems. Given the rapid advancements in AI, there are emerging discussions around AI Agents operating within an integrated ecosystem, paving the way for more autonomous and contextual AI-driven decision-making. So AI will evolve self aware and self sufficient.
My Personal Takeaway
In practice, the choice between supervised and unsupervised learning depends on the problem at hand and the availability of labeled data. While supervised learning provides precision and predictability, unsupervised learning excels in exploration and discovery. For me, the beauty lies in combining the two—leveraging supervised methods for predictive tasks and unsupervised methods to uncover hidden insights that fuel creativity and innovation.

By blending these approaches, I’ve not only improved the efficiency of my workflows but also expanded my perspective on what’s possible with machine learning. Each has its unique strengths, and together, they create a balanced toolkit for tackling diverse challenges.

Conclusion – Supervised Learning which is one of three types of machine learning. This post is limited to supervised learning to explorer its details i.e. what it is doing and can do for businesses as new electricity to power them up. This blog post I tried to performed a comparison of different supervised machine learning techniques in classifying FinTech data.
This blog post is an attempt to describes the best-known supervised techniques in relative detail but not to claim anything. The aim was to produce a lighter rephrase of supervised learning and review of the key ideas and not a simple list of all algorithms in this category.
#MachineLearning #SupervisedLearning
—
Points to Note:
All credits if any remains on the original contributor only. We have covered supervised and unsupervised machine learning where we make predictions from labelled historical data and find patterns from unlabeled data. In the past post, we have walked through unsupervised machine learning.
Books + Other readings Referred
- Research through Open Internet – NewsPortals, Economic development report papers and conferences.
- Internet-based survey results from 30 AI experts
- Personal experience of @AILabPage members.
Feedback & Further Question
Do you have any questions about Machine Learning, Deep Learning of AI? Leave a comment or ask your question via email. Will try my best to answer it.
============================ About the Author =======================
Read about Author at: About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your opinion / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter ====================================================================


[…] Supervised vs Unsupervised Machine Learning […]