Machine Learning Needs – Artificial intelligence and machine learning are like siblings—closely related, often mistaken for each other, but definitely not identical. Machine learning is the brilliant, hardworking younger sibling, a crucial subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and make decisions without being spoon-fed every instruction.

Today, ML shines because of its ability to devour massive amounts of data, spot patterns faster than a seasoned detective, and make predictions with uncanny accuracy. This power fuels everything from chatbots that sound almost human (but not quite) to recommendation engines that somehow know you better than you know yourself.
But let’s be honest—ML isn’t magic. It’s math, logic, and a lot of trial and error, wrapped in some seriously clever algorithms. It’s also evolving rapidly, moving toward self-learning systems that require less human babysitting.
In this post, I’ll break down ML in a way that’s simple, engaging, and—dare I say—fun. Whether you’re a beginner curious about how machines “learn” or a seasoned professional nodding along knowingly, let’s dive into this fascinating world together. No jargon overload, just an enjoyable learning experience with a few smiles along the way.
Machine learning is the hottest subject of today’s time, and being a data scientist is the sexiest job of today, but implementing these buzzwords in real-life business is the most important need.
Machine Learning Outlook
Machine learning is the hottest subject of today’s time, and being a data scientist is the sexiest job of today, but implementing these buzzwords in real-life business is the most important need. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence and a field of study that harnesses the principles of computer science and statistics. AILabPage members intuitively call statistics a graphical branch of mathematics.

The real need for today’s time and business is to clarify, demonstrate, and extract real values to benefit everyone from this golden keyword, “machine learning.” Why is ML so good today? For this, there are a couple of reasons, like those listed below, but not limited to them.

Although ML is magnificent implementing this bundle pack of ML for practical use in businesses is still a hurdle for many. ML’s current excellence can be explained by several reasons, such as those provided below although not exclusively.
- The explosion of big data
- Hunger for new business and revenue streams in this business shrinking times
- Advancements in machine learning algorithms
- Development of extremely powerful machine with high capacity & faster computing ability
- Storage capacity
As of today, sadly, most machine learning methods are based on supervised learning. Which means we still have a long way to go. In the Fintech domain, we say “machine learning” is the future (actually, that future is now) of “e-commerce,” and “data scientists” will work as batmen for “fintech” and “puretech.” Today’s machines are learning and performing tasks that were only done by humans in the past, like making better judgments and decisions, playing games, etc.
Lets Define Machine Learning
Machine learning is a focal point where business needs and experience (mathematics, statistics, and algorithmic logic/thinking) meet emerging technology and decide to work together to put useful results on the table for real business. Machine learning is also a subset of Artificial Intelligence. ML borrows principles from computer science and statistics, which are graphical branches of mathematics.
AILabPage defines Machine Learning as “A focal point where business, data and experience meets emerging technology and decides to work together“.
It instructs an algorithm to learn for itself by analyzing data. The more data it processes, the smarter the algorithm gets. Until only recently, even though the foundation was laid in 1950, ML remained largely confined to academia. Sadly, it’s becoming more accessible to developers as a tool. What we need is simply MLaaS (Machine Learning as a Service) for everyone. There are a couple of reasons. Machine learning entirely depends on algorithms of two kinds.
- Learning style
- Symmetry & similarity
Arthur Samuel coined it in 1959. He called it a “field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.” In our words, machine learning is a subject for real-life work outside of PhDs or scholarly books. At AILabPage, we define ML as follows:
Some History of Machine Learning
ML Arthur Samuel coined it in 1959. Some of the timelines of machine learning have evolved from an artificial intelligence subset to their own domain. It has reached an inflexion point, at least in terms of messaging. I remember in my school days, as part of statistics class, we were told something about AI and ML, and we laughed then, in the 1990s.

| Year | Concept | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1936 | Turing Machine | Alan Turing’s concept of a universal machine that laid the foundation for computational intelligence. |
| 1958 | Perceptron Model | Introduced by Frank Rosenblatt, an early model for artificial neurons. |
| 1950s-1980s | Symbolic AI | AI systems used symbolic rules and logic but struggled with real-world adaptability. |
| 1990s | Neural Networks Resurgence | Neural networks re-emerged with increased computing power, reviving interest in AI. |
| 2010s | Deep Learning Breakthrough | Enabled significant advances in image recognition, NLP, and self-learning AI. |
| Modern Era | Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Focuses on agents learning via rewards and penalties. |
| Modern Era | Generative Models (GANs, Transformers) | Enabled AI creativity. |
| Modern Era | AI-Augmented ML (AutoML, Meta-Learning) | Accelerates model optimization, reducing human intervention. |
Although machine learning has now gained prominence owing to the exponential rate (1990 was the flying gear year) of data generation and technological advancements to support it, it has roots in the old days. Major discoveries, achievements, milestones, and other major events are included in the picture here.
Types of Machine Learning
The approach to developing ML includes learning from data inputs based on “what has happened”. Evaluating and optimizing different model results remains the focus here.

As of today, machine learning is widely used in data analytics as a method to develop algorithms for making predictions on data. It is related to probability, statistics, and linear algebra. Machine learning is classified into three categories i.e. Supervised learning, Unsupervised learning, and Reinforcement learning, at a high level, depending on the nature of the learning and the learning system.

In a hypothetical situation, or most of the time (at least from our personal experience), the amount of data anyone will find may look like the picture above. We are talking about the volume of the data. The volume of data for supervised learning is the highest, and for reinforcement learning, it’s the lowest almost all the time.
Hierarchy of Machine Learning Needs
Excessive engagement in any activity can be counterproductive and lead to unintended consequences. There is no guarantee that rushing or completing tasks in their entirety will improve machine learning and artificial intelligence (ML/AI).

For example, installing a Ferrari engine in a non-specialized two-wheel-drive car would be impractical and unwise. Similarly, using advanced data analytics software may expedite the achievement of desired outcomes, but it does not guarantee accuracy.
To achieve optimal results, it is essential to collect accurate, relevant, and timely data that is organized, clean, tested, and optimized. This cyclical process may need to be repeated multiple times. Only after these efforts have been made is it time to test ML and AI solutions. The following are some additional points to consider:
- The quality of the data is critical. If the data is not accurate or relevant, the ML or AI models will not be able to learn effectively.
- The data must be organized and cleaned. This includes removing outliers, correcting errors, and filling in missing values.
- The data must be tested and optimized. This involves evaluating the performance of the ML and AI models and making adjustments as needed.
- The ML and AI solutions must be tested in a real-world setting. This is the only way to ensure that they will perform as expected.
By following these guidelines, organizations can maximize the benefits of ML and AI and avoid costly mistakes.
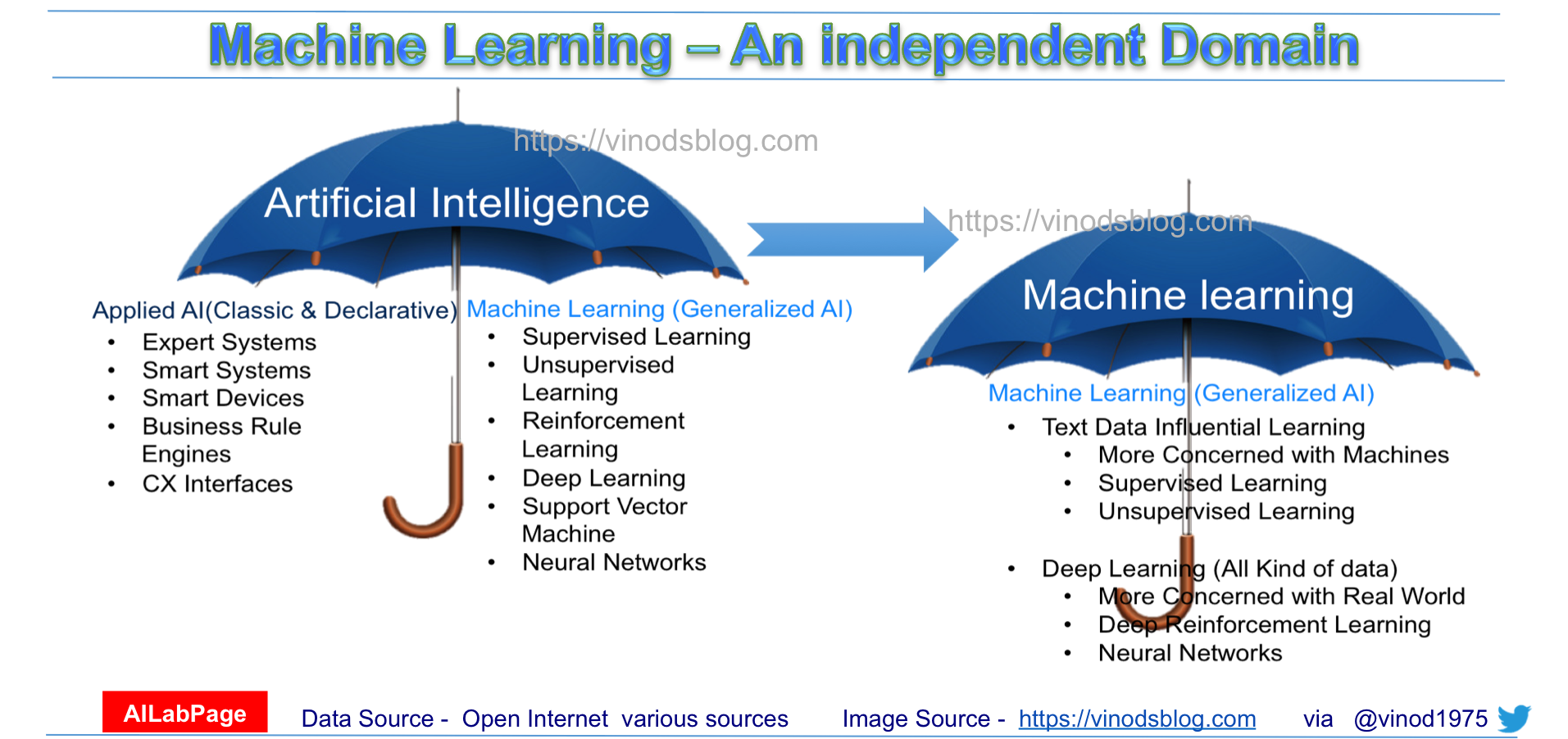
Machine Learning – An Independent Domain
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are two very hot buzzwords right now and often seem to be used interchangeably. In my best knowledge and experience, machine learning is growing at top speed and is going to make this statement true: “ML is not AI and has its own independent identity”. AI is all about smart devices and applications, but machine learning is all about learning and gaining accuracy. Maybe ML’s finished product can be called “AI.

| Aspect | Details | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Relation to AI | Machine learning is more aligned with generalized AI rather than applied AI. | ML operates within AI but has a distinct focus. |
| Definition Limitation | ML is not simply the emulation of human intelligence through algorithms. | ML is broader than mimicking human cognition. |
| Core Nature | ML differs significantly from natural intelligence and resembles synthetic model development. | ML follows a structured, model-driven approach. |
Anyway, our intention here is not to justify or show the difference between these two buzzwords but to prove machine learning is and is going to be independent of AI. Machine learning would mature into a mature enough technique (or set of techniques) independently that it would not need AI as a superset of it.
Machine Learning is not Magic
The complex amalgamation of various constituent elements, comprising data, mathematical computations, statistical analyses, algorithmic procedures, and computational proficiency, is conventionally referred to as “machine learning” in academic discourse.

So if not magic then what is it
- Machine learning involves systematic processes such as data collection, preprocessing, and feature engineering.
- Successful machine learning models require careful training and evaluation to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Model deployment is a crucial step in applying machine learning solutions to real-world problems.
- Understanding the underlying algorithms and techniques is essential for effective machine learning implementation.
- While machine learning can yield powerful insights, it is not a mystical solution and requires rigorous methodology and expertise.
The previously mentioned notion may be likened to the domain of wizardry, although it may also display similarities to the field of futurology, which involves the examination of feasible, credible, and attractive future possibilities. The examination of the fundamental perspectives and beliefs linked to machine learning is a subject of critical inquiry.
It is imperative to acknowledge that the progression of technology is not attributed to any mystical powers; instead, conventional tools such as MS Excel, Python, R, and cloud-based machine learning services from Azure and Amazon Web Services are utilized to eradicate such misconceptions. This topic exhibits an extraordinary level of clarity and simplicity, unencumbered by any necessity for memorization through repetition.
According to AILabPage, the aforementioned issue is unambiguous and as simple as consuming a serving of ice cream. This assertion is relevant not solely to individuals undertaking a doctorate program but also to all members of the community.
During a prior period, Microsoft embarked upon the integration of machine learning components onto the Azure platform. During that epoch, individuals experienced the sensation of being inundated and disorientated by the immense multitude of technological innovations and specialized jargon that permeated their environment.
The advent of Google’s TensorFlow and Cloud ML, coupled with Amazon’s foray into the realm of autonomous machine learning services, suggests a discernible trend towards the adoption of machine learning capabilities in the domain of cloud computing. The present state of affairs underscores the growing realization that machine learning is on the cusp of emerging as a substantial cloud computing phenomenon.
Real Life Use Cases
Machine learning is the process of a machine attempting to accomplish a task, independent of human intervention, more efficiently and more effectively with every passing attempt i.e learning phase.

At this point, AI- a machine which mimics the human mind, is still a pipe dream. In the middle, we have the meat of the pipeline, the model, which is the machine learning algorithm that learns to predict given input data.
ML is a sub-set of artificial intelligence (shouting for independence and getting there slowly) where computer algorithms are used to autonomously learn from data and information. Machine learning, however, has been a reality in our lives for quite some time.
Deep learning is a subcategory of machine learning algorithms that use multi-layered neural networks to learn complex relationships between inputs and outputs.
Machine Learning to bring – Data Intelligence as a Service
In the coming years, data intelligence services will be the most prominent application that will be provisioning prototypes for security measures to truly fortify DIaaS.

There are certain market dynamics that determine the growth of data and its related analytics. That’s where data intelligence’s adaptive dynamics come into play to assess the factors driving the organization to adapt their existing, profitable lines of business. This helps them stay relevant in the rapidly evolving future of the world and is an enormous help for the Blue Ocean Shift strategy.
In the context of machine learning, the conventional methodology involves generating distinct train-and-test partitions of the dataset, which may be accomplished through the use of cross-validation techniques. The process of loading all training data into the main memory, followed by the computation of a model from said data, may necessitate multiple passes. The present depiction is delineated in this communication.
Machine Learning use cases for Info-Security (#GDPR)
Machine learning can help automate more menial tasks previously carried out by IT or network security teams that are neither qualified nor skilled for this type of information security, especially in financial system data security.

In principle, machine learning can help businesses better analyze threats and respond to attacks and security incidents. The results of ML protecting data are astonishing, and ML as an info-security guard is much better than any human. Thusly, machine learning in information security involves quickly developing and detecting anomalies in patterns.
I guess we have now done enough drumming for machine learning and all those learnings around it; it’s time to take some action and get this done on the ground for our real and daily use.
The realm of machine learning is expanding at a notable pace and has emerged as a crucial tool in various domains, including web search, advertisement placement, credit assessment, and stock trading, among others.

Conclusion – This article explores the implementation of machine learning techniques utilizing computer algorithms to identify patterns within datasets. Such patterns are then used to make predictions and informed decisions in real-world scenarios. As a specific application, the utilization of machine learning within healthcare settings, specifically in genomics and preterm birth, is examined. The objective is to uncover latent topics within voluminous document repositories via topic modeling methodologies. The succeeding blog entries shall explicate the answers to the aforementioned inquiries.
—
Points to Note:
All credits, if any, remain with the original contributor only. We have now summarized our last four posts here to give a quick glimpse. You can find previous posts on machine learning (the helicopter view), supervised machine learning, unsupervised machine learning, and reinforcement learning links.
Books + Other readings Referred
- Research through the open internet, news portals, white papers, and imparted knowledge via live conferences and lectures. Lab and hands-on experience of @AILabPage (Self-taught learners group) members.
- Machine Learning – An Introduction and Machine Learning -A Probabilistic Perspective
Feedback & Further Question
Do you need more details or have any questions on topics such as technology (including conventional architecture, machine learning, and deep learning), advanced data analysis (such as data science or big data), blockchain, theoretical physics, or photography? Please feel free to ask your question either by leaving a comment or by sending us an via email. I will do my utmost to offer a response that meets your needs and expectations.
============================ About the Author =======================
Read about Author at : About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your feedback / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter ====================================================================

[…] […]
[…] above structure is created to improve a machine learning system. CNN’s also allows for working with inputs of variable size and efficiently describe […]
[…] above structure is created to improve a machine learning system. CNN’s also allows for working with inputs of variable size and efficiently describe complicated […]
[…] above structure is created to improve a machine learning system. CNN’s also allows for working with inputs of variable size and efficiently describe complicated […]
[…] Astonishing Hierarchy of Machine Learning Needs […]
[…] To read the whole article, with illustrations, click here. […]
[…] Astonishing Hierarchy of Machine Learning Needs […]
[…] Astonishing Hierarchy of Machine Learning Needs […]
[…] Machine Learning – How What and Why […]
[…] Astonishing Hierarchy of Machine Learning Needs […]
[…] Machine Learning – How What and Why […]
[…] Machine Learning – How What and Why […]
[…] Machine Learning – How What and Why […]