Recurrent Neural Networks: Ever had that moment where you’re typing a text, and your phone suddenly finishes your sentence like it’s been eavesdropping on your thoughts? “How did it know I was about to say ‘I’ll be there in 5’?!” Spoiler alert: it’s not magic (though it feels like it). It’s an RNN—Recurrent Neural Network—flexing its brainy muscles behind the scenes. Whether you’re texting your bestie about weekend plans, drafting a very passive-aggressive email (we’ve all been there), or Googling “why is my WiFi so slow” for the 47th time, RNNs are the unsung heroes predicting your next move.

So, what’s the deal with RNNs? Why are they cooler than your average neural network? Well, regular neural networks are like goldfish—they see every input as a brand-new thing, completely forgetting what came before. But RNNs? They’ve got memory. Like that one friend who still brings up that time you tripped in front of your crush in 8th grade (thanks, Kavita), RNNs remember stuff. They have these loops that keep past information alive, so they can spot patterns over time. It’s like they’re saying, “Hey, I’ve seen this before. Let me help you out.”
This memory superpower makes RNNs the MVPs of anything involving sequences—speech recognition, language translation, even generating music that doesn’t sound like a robot’s existential crisis. Instead of starting from scratch every time, they reuse what they’ve already learned, making smarter, more context-aware decisions. It’s like they’re the AI version of, “Oh, you’re talking about that again? Let me save you some time.”
Now, if you’re here for a deep dive into the math behind RNNs, I’m gonna stop you right there. This isn’t that kind of party. No brain-melting formulas, no PhD-level jargon—just a chill, relatable chat about how these things work. If you finish reading this and think, “Okay, I kinda get it now,” then my job here is done.
As per the experience from AILabPage’s lab sessions, we can conclude and say – One lesser-known fact about Recurrent Neural Networks is their ability to perform dynamic computation on sequences of data, allowing them to capture temporal dependencies effectively.
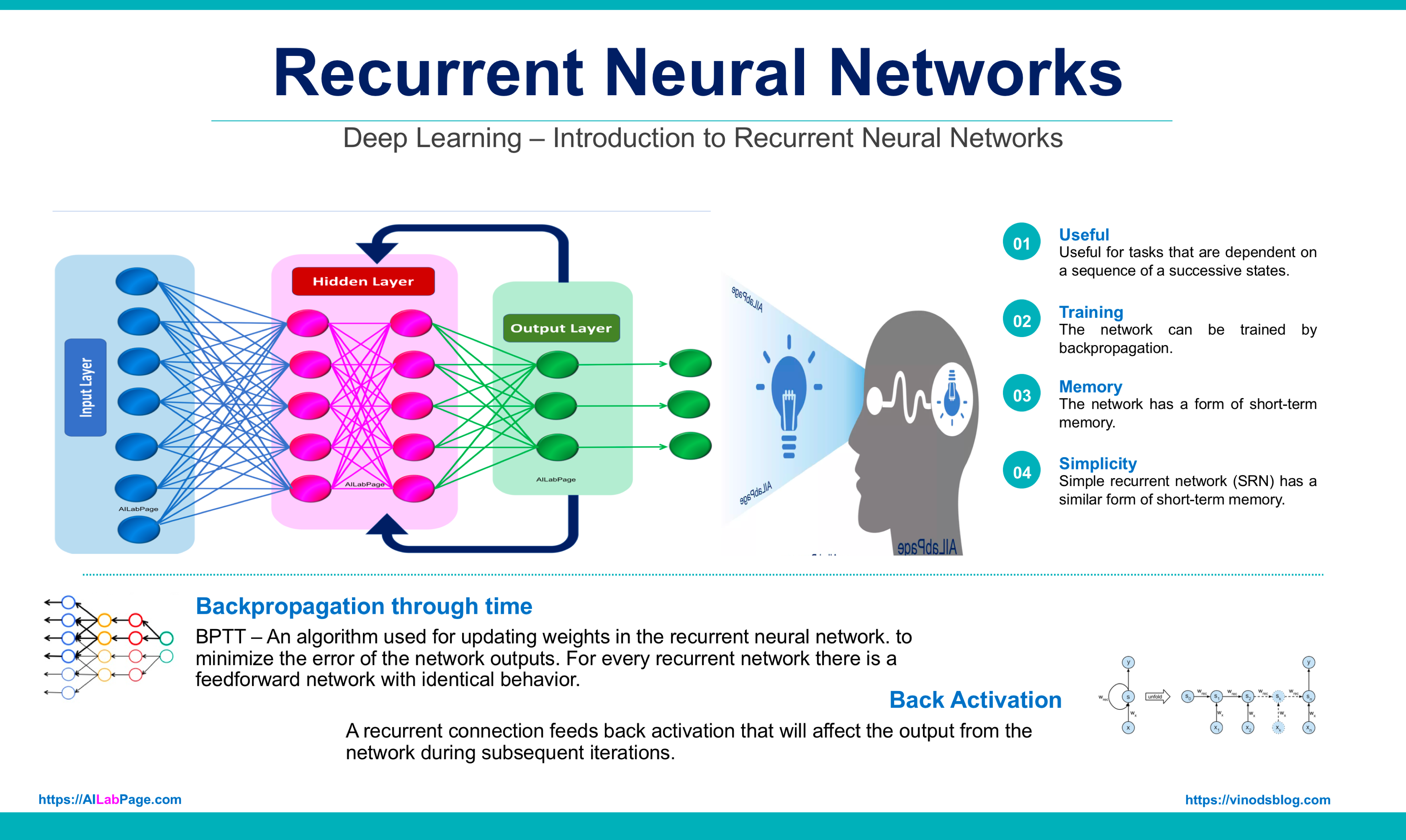
Artificial Neural Networks – What Is It
Back in 1943, McCulloch and Pitts had a wild idea: “What if machines could think like brains?” They built the first neural network—super basic, but a start. Fast forward, and we now have Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), the tech behind your phone’s eerily good text predictions.
Unlike regular artificial neural networks, which forget everything instantly, RNNs remember past inputs. This makes them great for speech recognition, language translation, and even AI-generated music that doesn’t sound like a robot’s midlife crisis. Think of it this way: a basic neural net reads texts one by one, clueless about context. An RNN? It follows the whole conversation. That’s why when you type “Happy,” your phone suggests “birthday”—not “potato.”

It is important to note that artificial neural networks are way different from computer programs, so please don’t get the wrong perception from the above definition. Neural networks consist of input and output layers and at least one hidden layer. There are several kinds of Neural Networks in deep learning.

As per AILabPage, Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are “Complex computer code written with several simple, highly interconnected processing elements that is inspired by human biological brain structure for simulating human brain working and processing data (Information) models”.
- Multi-Layer Perceptron
- Radial Basis Network
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Generative Adversarial Networks
- Convolutional Neural Networks.
Training neural networks isn’t just hard—it’s an unpredictable rollercoaster of complexity, frustration, and occasional eureka moments. Every data scientist knows this struggle like a chef battling a stubborn soufflé. And at the heart of this chaos? Weights.
In neural networks, weights don’t just sit there like passive numbers; they’re deeply tangled with hidden layers, influencing every single computation, like a puppeteer pulling a thousand invisible strings. Get them right, and your model shines. Get them wrong, and, well… welcome to the abyss of vanishing gradients! The process of training a neural network boils down to three crucial steps—each as vital as the next, and each demanding patience, precision, and a touch of insanity. Let’s dive in.
- Forward pass and makes a prediction.
- Compare prediction to the ground truth using a loss function.
- Error value to do backpropagation
The algorithm to train ANNs depends on two basic concepts: first, reducing the sum squared error to an acceptable value, and second, having reliable data to train the network under supervision.
Recurrent Neural Networks- Outlook
Recurrent neural networks are not too old neural networks, they were developed in the 1980s. One of the biggest uniquenesses RNNs have is their “UAP” (universal approximation property), so they can approximate virtually any dynamical system.

This unique property forces us to say that recurrent neural networks have something magical about them.
- RNNs takes input as time series and provide an output as time series,
- They have at least one connection cycle.
There is a strong perception of the recurrent neural network training part. The training is assumed to be super complex, difficult, expensive, and time-consuming.

As a matter of fact, after a few hands-on experiences in our lab, our response is just the opposite. So common wisdom is completely opposite from reality. The robustness and scalability of RNNs are super exciting compared to traditional neural networks and even convolutional neural networks.

Recurrent Neural Networks are way more special as compared to other neural networks. Non-RNN APIs have too many constraints and limitations (sometimes RNNs also do the same, though). Non-RNN API take
- Input – Fixed size vector: For example an “image” or a “character”
- Output – Fixed size vector: Probability matrix
- Size of Neuron – Fixed number of layers / computational steps
We need to answer “What kind of problems can be solved with “Recurrent Neural Networks”? before we go any deeper in this.
Understanding the Need for Sequential Data Processing
When we think about human intelligence, one of its most fundamental aspects is understanding sequences—whether it’s comprehending spoken language, reading a book, recognizing patterns in stock markets, or even predicting the next note in a melody. Traditional neural networks, despite their ability to learn complex relationships, lack a natural mechanism to handle sequential dependencies.

At AILabPage, our journey into Deep Learning has always been fueled by curiosity and a relentless pursuit of practical, real-world solutions. When we first started working on temporal data problems, it quickly became clear that standard feedforward neural networks (FNNs) were not sufficient for tasks where context matters. Imagine trying to predict the next word in a sentence without considering previous words—it’s like playing chess without remembering past moves!
Sequential data—where each element is dependent on past inputs—demands a specialized approach. In mathematical terms, if we define input data as a sequence: X = {x1,x2,…,x3}.
then our prediction at any timestep t should be influenced not just by xtx_txt, but also by all preceding inputs {x1,x2,…,xt−1}. This is where Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) shine.
How RNNs Differ from Traditional Neural Networks
Unlike traditional Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs), which process data in a one-time, static manner, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) introduce the concept of memory—allowing them to retain past information and use it for future predictions.

Key Difference: Memory & Loops
In a traditional neural network, information moves in a single, straightforward path—from input through hidden layers to the final output—without the ability to look back or retain past knowledge. There’s no built-in mechanism for feedback or memory retention, making each input independent of previous ones. Mathematically, a Feedforward Neural Network (FNN) operates as:
Y = f(WX + b)
Here, W represents the weight matrix, X is the input, and b is the bias term. However, unlike FNNs, a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) introduces a feedback loop, allowing past states to actively shape and influence the current prediction. This memory-driven approach makes RNNs more adaptive to sequential patterns and contextual understanding.
ht = f(Wxt+Uht−1 + b)
Here, hₜ represents the hidden state at time step t, which retains information from previous time steps through the weight matrix U. This ability to remember and leverage past data empowers Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) to effectively capture temporal dependencies, making them exceptionally suited for tasks involving sequences, patterns, and contextual learning.

| Feature | Feedforward Neural Network (FNN) | Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) | Diagram Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Flow | One-way (input → output) | Loops & feedback connections | FNN → Math 🔗 RNN → Math |
| Mathematical Flow | Single direction flow | Loops & memory | FNN → Math 🔗 RNN → Math |
| Memory & Feedback | No feedback, no memory | Retains past states | FNN → Memory 🔗 RNN → Memory |
| Mathematical Formula | Y=f(WX+b)Y = f(WX + b)Y=f(WX+b) | ht=f(WXt+Uht−1+b)h_t = f(WX_t + Uh_{t-1} + b)ht=f(WXt+Uht−1+b) | Diagram Notes on FNN & RNN |
| Analogy | Student memorizing answers (memorizes answers) | Detective solving a case (uses past clues) | FNN → Analogy 🔗 RNN → Analogy |
| Best For | Independent tasks | Sequential tasks | Implicit from Memory Node |
| Stock Prediction | Random-like guesses | Learns market trends (market trend awareness) | FNN → StockPrediction 🔗 RNN → StockPrediction |
Think of it like this:
- A Feedforward Neural Network is like a student memorizing answers without context.
- A Recurrent Neural Network is like a detective piecing together clues from past evidence to solve a case.
At AILabPage, we put this to the test with stock price predictions, where the next day’s price is shaped by past trends. When using Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs)—which lack memory—the predictions were no better than random guesses. However, with Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), patterns began to surface. The model started to “remember” market movements, recognizing trends and making more informed predictions. This demonstrated the true power of memory in AI-driven forecasting!
Real-World Applications of RNNs
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) aren’t just fancy math—they’re the secret sauce behind some of the coolest AI applications out there. These bad boys thrive on sequential data, making them the go-to choice for anything that unfolds over time, like a gripping Netflix series or your unpredictable stock portfolio.

| # | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Chatbots | – RNN-based architectures process words sequentially to understand intent. – Example: Predicting the next word in a sentence: P(“morning” ∣ “Good”) > P(“banana” ∣ “Good”) – The network learns language structures over time. |
| 2. | Speech Recognition & Audio Processing | – Humans process words as a sequence, not in isolation. – Powers technologies like Google Voice, Alexa, and real-time transcription services. – Example: At AILabPage, we trained an RNN to recognize spoken digits, mapping audio waveforms to numerical outputs. |
| 3. | Financial Time-Series Prediction | – Stock prices, cryptocurrency trends, and sales forecasting depend on past data. – Traditional ML models treat each price as independent, while RNNs capture sequential patterns. – Example: We applied an LSTM (a type of RNN) to predict currency exchange rates, significantly outperforming static models. |
| 4. | Anomaly Detection in IoT & Cybersecurity | – Detecting fraud, cyber threats, and system failures requires monitoring events over time. – RNNs learn normal behavior and detect anomalies based on sequential deviations. |
RNNs aren’t just another deep learning technique—they are the backbone of sequential intelligence. Whether you’re dealing with text, audio, finance, or IoT data, if the order of data matters, RNNs (and their advanced versions like LSTMs and GRUs) offer unparalleled learning power.
At AILabPage, we embrace a learn-by-doing philosophy, where every experiment contributes to a deeper understanding. The journey of RNNs is like life itself—constantly learning from the past to make better decisions in the future.
Fundamentals of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
At AILabPage, we’ve spent countless hours experimenting with AI architectures, and one thing became crystal clear—not all data is independent. When processing sequential data (like time-series, speech, or language), traditional neural networks fall short because they forget past inputs. That’s where Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) shine!

Unlike standard neural networks that treat each input as independent, RNNs remember past information through hidden states. Think of it like a human brain—when reading a sentence, you don’t process each word in isolation; you retain context to understand meaning.
The Concept of Memory in Neural Networks
Memory is the quintessential feature that sets RNNs apart. Traditional feedforward networks process inputs in a linear fashion—left to right, one at a time. RNNs, on the other hand, loop back information from previous time steps, creating a memory effect.

🔹 Mathematical Insight:
At any given time step t, the hidden state h is computed as:
ht = f(Whht−1 + WxXt)
where:
- ht is the current hidden state,
- Wh is the weight applied to the previous hidden state,
- Xt is the input at time t,
- f is the activation function (typically tanh or ReLU).
This recursive process allows past information to influence future predictions—a game-changer for sequential tasks!
Structure and Architecture of an RNN
An RNN is fundamentally different from a traditional neural network. Instead of a simple input → hidden → output structure, RNNs introduce loops that allow information to persist. Here’s how it works:

- The network receives an input Xt at time step t.
- The hidden state ht updates using past information.
- The output is computed and passed forward while the hidden state is retained for the next time step.
💡 Example from AILabPage:
We trained an RNN to predict daily temperature trends. Instead of relying solely on the previous day’s temperature, it considered multiple past days to forecast future values accurately. This sequential dependency was impossible for traditional ML models to capture effectively.
Forward and Backward Pass in RNNs
Understanding how RNNs learn is key to grasping their power. Training an RNN involves:

- Forward Pass:
- Input Xt flows through the network.
- The hidden state ht stores past information.
- The network computes an output.
2. Backward Pass (Backpropagation Through Time – BPTT):
- Errors are propagated backward through time, meaning each time step’s error affects previous time steps.
- We apply gradient descent to update weights.
The gradient of the loss with respect to weights is calculated using the chain rule, leading to updates in earlier time steps—this is why it’s called Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT).concerning
- Mathematical Insight:
The loss function L is computed as
L = T∑t=1 Lt
Challenge: RNNs suffer from vanishing gradients, where earlier layers receive almost no meaningful updates. That’s why we turn to LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) and GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units) to fix this!
Supervised or Unsupervised
RNNs are versatile models applicable to both supervised and unsupervised learning. In supervised tasks, they learn from labeled input-output pairs to make predictions or classifications. In unsupervised tasks, they discover patterns or generate sequences without explicit labels. Their adaptability depends on the problem type and data structure.

| Learning Type | Description | Examples | Techniques/Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | RNNs are trained with labeled data, where input-output pairs are explicitly provided. The goal is to map input sequences to output sequences or discrete labels. | – Sequence Prediction: Time series forecasting, language modeling, speech recognition – Sequence Classification: Sentiment analysis, named entity recognition | – Minimizing loss functions through optimization algorithms like Adam or SGD – Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT): Adapts weights over time steps – Use of advanced cells such as LSTM (handles long-term dependencies) or GRU (simpler and computationally efficient) to overcome the vanishing gradient problem inherent in RNNs. |
| Unsupervised Learning | RNNs are applied to unlabeled data, learning patterns, or generating sequences without explicit supervision. The focus is on discovering structures and relationships in the data. | – Sequence Generation: Generating text, audio, or videos – Sequence-to-Sequence Learning: Machine translation, text summarization – Anomaly Detection: Identifying irregular patterns in financial transactions, network activity, or sensor data | – Uses techniques like unsupervised pretraining followed by fine-tuning – Models like autoencoders or variational autoencoders (VAEs) for sequence generation – Identifies deviations using probabilistic measures or reconstruction errors – Leverages attention mechanisms in sequence-to-sequence models for better context and accuracy. |
In summary, while RNNs are commonly used in supervised learning settings where labeled data is available, they are versatile enough to be applied to a variety of unsupervised learning tasks as well.
Recurrent Neural Network- Architecture
A typical neural network comprises an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. RNNs, tailored for sequential data, incorporate an additional feedback loop in the hidden layer known as the temporal loop. This loop allows the network to retain information from previous inputs, enabling it to process sequential data effectively. The types of RNN architectures include

- One to One: Basic RNNs supporting a single input and output, akin to conventional neural networks.
- One to Many: Featuring one input and multiple outputs, useful for tasks like image description.
- Many to One: Involving multiple inputs and a single output, suitable for sentiment analysis.
- Many to Many: Supporting multiple inputs and outputs, ideal for tasks like language translation, requiring sequence retention for accuracy.

:
| Step | From → To | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | User → Input Sequence | Provide Input Sequence |
| 2 | Input Sequence → Embedding Layer | Pass Input Sequence |
| 3 | Embedding Layer → Word Embedding | Generate Word Embeddings |
| 4 | Embedding Layer → Positional Encoding | Add Positional Encoding |
| 5 | Embedding Layer → RNN Cell | Pass Embedded Input |
| 6 | RNN Cell → Hidden State | Compute Hidden State |
| 7 | RNN Cell → Weight Matrix (W) | Apply Weight Matrix |
| 8 | RNN Cell → Bias (b) | Add Bias |
| 9 | RNN Cell → Activation Function | Apply Activation Function |
| 10 | Activation Function → Tanh | Apply Tanh |
| 11 | Activation Function → ReLU | Apply ReLU |
| 12 | Activation Function → Output Layer | Pass Activated Output |
| 13 | Output Layer → Softmax | Compute Probabilities |
| 14 | Softmax → Predicted Output | Generate Predicted Output |
| 15 | Predicted Output → Loss Calculation | Compute Loss |
| 16 | Loss Calculation → Cross Entropy | Cross Entropy Loss |
| 17 | Loss Calculation → Mean Squared Error | Mean Squared Error Loss |
| 18 | Loss Calculation → BPTT | Calculate Gradient |
| 19 | BPTT → Gradient Descent | Perform Gradient Descent |
| 20 | BPTT → Weight Update | Update Weights and Biases |
| 21 | Weight Update → RNN Cell | Update RNN Parameters |
| 22 | Predicted Output → End | Output Predicted Sequence |
From their architecture’s inherent ability to capture temporal dependencies to their applications in diverse fields like NLP and time series prediction, RNNs offer a powerful framework for analyzing dynamic data streams. Understanding the architecture of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) requires familiarity with artificial feed-forward neural networks.
Recurrent Neural Network Variants
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Recursive Neural Networks (ReNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) can be considered as part of the broader family of neural network architectures designed for handling sequential data.

| Architecture | Key Characteristics | Purpose | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNNs | – Share recurrence characteristic – Capture temporal dependencies in sequential data | – Handle time series, language, and speech data | – Stock price prediction – Sentiment analysis – Speech-to-text |
| GRUs | – Simplified version of LSTM – Less computationally expensive – Capture sequential dependencies | – Efficient for sequential data modeling | – Predictive text generation – Weather forecasting – Speech recognition |
| LSTMs | – More complex than RNNs and GRUs – Use memory cells and gates to store and forget information – Capture long-term dependencies | – Handle long-term dependencies in sequences | – Language translation – Video captioning – Time series forecasting |
| ReNNs | – Involve recurrence – Tailored for hierarchical data structures such as trees or graphs | – Work with structured data (e.g., graphs, trees) | – Natural language parsing – Semantic analysis – Graph-based recommendation systems |
| Differences | – RNNs, GRUs, LSTMs are for sequential data – ReNNs are specifically for hierarchical data structures like trees or graphs | – ReNNs specialize in structured data, others focus on sequences | – Hierarchical data modeling – Tree/graph traversal tasks |
| Use Cases | – Time series forecasting – Speech recognition – Language modeling | – ReNNs are used in tree structures and graph data processing | – ReNNs for parsing structured data – LSTMs for long-term sequence learning |
In this sense, RNNs, GRUs, LSTMs, and ReNNs form a cohesive family of architectures within the realm of neural networks, each offering different capabilities for processing sequential or structured data. However, within this family, there are distinct variations and design choices that cater to specific data characteristics and modeling requirements.
Solving Complex Problems with Sequential Data
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are well-suited for solving a wide range of problems that involve sequential or time-series data. Some of the key problems that can be effectively addressed using RNNs include

- Natural Language Processing (NLP): RNNs are commonly used in tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis, text generation, and speech recognition. Their ability to capture temporal dependencies in language sequences makes them valuable for understanding and generating human language.
- Time Series Analysis: RNNs are ideal for time series prediction and forecasting, enabling accurate predictions based on historical data. They can be applied to financial forecasting, stock market analysis, weather prediction, and other time-dependent data analysis tasks.
- Speech Recognition: RNNs excel in converting spoken language into written text. They can process audio data over time to recognize speech patterns and convert them into textual representations.
- Music Generation: RNNs can be used in music composition and generation tasks. By learning patterns and structures from existing music, RNNs can create new musical pieces that follow similar styles and harmonies.
- Video Analysis: RNNs can be applied to video analysis tasks, such as action recognition, object tracking, and activity forecasting. They can process sequential frames of a video to understand temporal patterns and movements.
- Natural Language Generation: RNNs can generate coherent and contextually relevant text based on given prompts or input, making them useful in chatbots, automatic summarization, and creative writing applications.
- Sentiment Analysis: RNNs can determine the sentiment of a given piece of text, classifying it as positive, negative, or neutral, which is valuable for sentiment analysis in customer feedback and social media data.
- Gesture Recognition: RNNs can recognize gestures from motion capture data, making them applicable in virtual reality and human-computer interaction systems.
These are just a few examples of the diverse problems that RNNs can effectively solve. Their ability to handle sequential data and capture temporal dependencies makes them a powerful tool for a wide range of real-world applications across various industries.
When we deal with RNNs, they show excellent and dynamic abilities to deal with various input and output types. Before we go deeper, let’s look at some real-life examples.

- Varying Inputs and Fixed Outputs: Speech, Text Recognition, and Sentiment Classification: In today’s time, this can be the biggest relief for a bomb like social media to kick out negative comments. People who like to give only negative comments for anything and everything rather than helping have one motive: to pull him/her down) someone’s efforts. Classifying tweets and Facebook comments into positive and negative sentiments becomes easy here. Inputs with varying lengths, while the output is of a fixed length.

- Fixed Inputs and Varying Outputs: AILabPage’s Image Recognition (Captioning) transcends visual comprehension barriers. Employing advanced algorithms, it interprets single-input images, producing detailed captions. From lively scenes of children riding bikes to serene park moments and dynamic sports activities like football or dancing, its output flexibility accommodates varied contexts. AILabPage’s pioneering solution redefines image processing capabilities, promising versatile applications across industries, from enhancing accessibility for visually impaired individuals to streamlining content indexing for businesses.

- Varying Inputs and Varying Outputs: Varying Inputs and Varying Outputs: AILabPage’s Machine Translation and Language Translation revolutionize cross-lingual communication. Human translation, a laborious endeavor, is surpassed by innovative algorithms. AILabPage’s solution, akin to Google’s online translation, excels in holistic text interpretation. It not only conveys words but also preserves sentiments, adapts to varied input lengths, and contextualizes meanings. This transformative capability extends to both input and output variations, promising enhanced language accessibility and seamless global communication.
As evident from the cases discussed above, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) excel at mapping inputs to outputs of diverse types and lengths, showcasing their versatility and broad applicability.

The underlying foundation of RNNs lies in their ability to handle sequential data, making them inherently suitable for tasks involving time series, natural language processing, audio analysis, and more. The generalized nature of RNNs allows them to adapt and learn from temporal dependencies in data, enabling them to tackle a wide range of problems and deliver meaningful insights in various domains.
Their capacity to capture context and temporal relationships in sequential data makes RNNs a valuable tool for addressing real-world challenges, where the length and complexity of input-output mappings may vary considerably. By leveraging this inherent flexibility, developers and researchers can employ RNNs as a fundamental building block for constructing innovative and sophisticated models tailored to their specific data-driven needs.
Recurrent Neural Networks & Sequence Data
As we know by now, RNNs are considered to be fairly good for modeling sequence data. Let’s understand sequential data a bit. While playing cricket, we predict and run in the direction where the ball moves. This means recurrent networks take current input examples they see and also what they have perceived previously in time. This happens without any guessing or calculation because our brain is programmed so well that we don’t even realize why we run in a ball’s direction.

If we look at the recording of ball movement later, we will have enough data to understand and match our action. So this is a sequence—a particular order in which one thing follows another. With this information, we can now see that the ball is moving to the right. Sequence data can be obtained from
- Audio files: This is considered a natural sequence. Audio file clips can be broken down in the audio spectrogram and fed into RNNs.
- Text file: Text is another form of sequence; text data can be broken into characters or words (remember search engines guessing your next word or character).
Can we comfortably say that RNNs are good at processing sequence data for predictions based on our examples above? RNNs are gaining more attraction and popularity for one core reason: they allow us to operate over sequences of vectors for input and output, not just fixed-size vectors. On the downside, RNNs suffer from short-term memory.
Use cases – Recurrent Neural Networks
Let’s understand some of the use cases for recurrent neural networks. There are numerous exciting applications that got a lot easier, more advanced, and more fun-filled because of RNNs. Some of them are listed below.
- Music synthesis
- Speech, text recognition & sentiment classification
- Image recognition (captioning)
- Machine Translation – Language translation
- Chatbots & NLP
- Stock predictions
To comprehend the intricacies of constructing and training Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), including widely utilized variations like Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, it is essential to delve into the fundamental principles and underlying mechanisms of these sophisticated architectures.

Mastering the art of RNNs entails grasping the concept of sequential data processing, understanding the role of recurrent connections in retaining temporal information, and exploring the challenges posed by vanishing or exploding gradients.
| Topic | Details | AILabPage Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Empowering Innovation with RNNs | RNNs help solve real-world challenges like natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, and time series analysis by leveraging sequential data. | We emphasize practical learning to help developers and researchers master these techniques for real-world AI applications. |
| Learning Opportunities | Many free and paid courses are available online for learning RNNs. | At AILabPage, we provide hands-on classroom training in our labs, ensuring deep learning enthusiasts gain real implementation experience. |
| Applications & Project Building | RNNs are widely used for text synthesis, machine translation, and predictive modeling. | Our training programs focus on industry-relevant projects, allowing learners to build cutting-edge deep learning applications. |
| Variations of RNNs | Advanced architectures like LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory), GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units), and Bidirectional RNNs improve memory retention and predictive accuracy. | We guide learners through practical experiments and real-world datasets, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of RNNs and their applications. |
These sequence algorithms have significantly simplified the process of constructing models for natural language, audio files, and other types of sequential data, making them more accessible and effective in various applications.
Vanishing and Exploding Gradient Problem
The deep neural network has a major issue around gradients as it is very unstable. Due to its unstable nature, it tends to either explode or vanish from earlier layers quickly.

The vanishing gradient problem emerged in the 1990s as a major obstacle to RNNs’ performance. In this problem, adjusting weights to decrease errors and the “synch problem” lead the network to cease to learn at the very early stage itself.
The problem encountered by Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) had a significant impact on their popularity and usability. This issue arises from the vanishing or exploding gradients phenomenon, which occurs when the RNN attempts to retain information from previous time steps. The nature of RNNs to maintain a memory of past values can lead to confusion, causing the current values to either skyrocket or plummet uncontrollably, overpowering the learning algorithm.

As a result, an undesirable situation of indefinite loops arises, disrupting the network’s ability to make further progress and effectively bringing the entire learning process to a standstill. This challenge posed significant obstacles to the practical application and widespread adoption of RNNs, prompting researchers and developers to seek alternative architectures and techniques, such as LSTMs (Long Short-Term Memory) and GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units), which have proven more effective in addressing the vanishing and exploding gradient issues while preserving the temporal dependencies in sequential data.
For example, neurons might get stuck in a loop where they keep multiplying the previous number by a new number, which can go to infinity if all numbers are more than one or get stuck at zero if any number is zero. And it depends on how much time you have. For us at AILabPage, we say machine learning is a crystal-clear and simple task. It is not only for PhD aspirants; it’s for you, us, and everyone.
Backpropagation in a Recurrent Neural Network (BPTT)
In the ever-evolving landscape of machine learning, Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT) stands out as a crucial technique for training Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). From my experience as a technology leader, I’ve seen firsthand how mastering BPTT can unlock new levels of performance in models dealing with sequential data.

Understanding BPTT
BPTT extends the classic backpropagation algorithm into the realm of time series data by “unfolding” the RNN across its time steps. This unfolding enables the calculation of gradients over multiple time steps, which is essential for learning long-term dependencies in sequences.
Key Phases of BPTT:
- Forward Pass: In this phase, the RNN processes the input sequence, updating its hidden states and generating outputs. Each step in the sequence affects the subsequent hidden states, making it crucial to accurately capture these dependencies.
- Backward Pass: Here, BPTT calculates gradients by traversing back through the unfolded time steps. This process involves computing the gradients of the loss function concerning the network’s weights and accumulating these gradients to update the weights effectively.
- Challenges and Solutions: While BPTT is powerful, it’s not without its challenges. The vanishing and exploding gradient problems can significantly impact the training process. Solutions such as gradient clipping and advanced optimization techniques help mitigate these issues, ensuring stable and effective learning.

BPTT is a foundational technique in training RNNs, enabling these networks to learn complex, sequential dependencies. My experience highlights the importance of understanding both the power and the limitations of BPTT. As technology continues to advance, mastering these techniques and their associated challenges will be crucial for driving innovation and achieving excellence in machine learning applications.
GRUs and RNNs
Gated Recurrent Units and variant of the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) architecture designed to overcome the challenges posed by the vanishing gradient problem.

The GRU model demonstrates commensurate performance with the LSTM model, notwithstanding its less intricate architecture. The Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) functions via the integration of the memorization and hidden state components into a concatenated vector, effectively eliminating the requirement for separate memory cells. The GRUs offer two distinct gates, specifically the update gate and the reset gate.
By now we know the GRU is a unique neural network architecture that differs from conventional RNNs, aiming to understand the intricate and long-term connections within sequential data while maintaining a simpler structure as compared to the LSTM.

- Hidden State: The idea of a hidden state is related to the outcome generated by the GRU component.
- It signifies how data is shared with upcoming time phases or interconnected layers in the neural network.
- The main factor that affects things is the way in which the original information combines with the changes in memory, which is determined by the update gate.
- Current Memory State: The current condition of memory relates to the knowledge that has been remembered and conserved in the current moment.
- The present iteration of the text is dependent upon the employment of the reset gate, which serves the purpose of regulating the relevance of past recollections, and the update gate.
- This is responsible for supervising the quantity of new information that is meant to be assimilated.
Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) have gained significant recognition for their efficacy in multiple natural language processing (NLP) undertakings, including but not limited to machine translation, sentiment analysis, and text generation.
The simplified structure of the GRUs renders it computationally less expensive than LSTM. The decision to select either long-short-term memory (LSTM) or gated recurrent units (GRU) hinges upon the particular task, dataset, and computational resources that are at one’s disposal, as each architecture may prove to be efficacious in distinct circumstances.
LSTM and RNNs
Long Short-Term Memory – LSTM, is an optimized RNN for gradient issues. RNNs can model sequences thanks to cyclic connections, unlike feedforward neural networks. Models successful at sequence labeling and prediction. Despite being widely used, RNNs are underutilized in speech recognition, mainly for minor phone recognition tasks. New RNN architectures use LSTM to improve speech recognition training for large lexicons.

Long Short-Term Memory Networks are the heart of many modern deep learning applications, especially when it comes to tasks involving sequential data.
LSTM is a popular technique used in various disciplines, such as sentiment analysis, language generation, speech recognition, and video analysis. The system includes memory units and mechanisms to determine important information for long-term storage. LSTMs includes a distinctive design methodology used for recurrent neural networks (RNNs) with the objective of surmounting the limitations of conventional RNNs in identifying complex patterns within sequential data.

By working together in harmony, the individual parts come together to enhance the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) design’s ability to learn and retain information over long periods of time. This ultimately results in its capability to effectively handle and integrate sequential data with consistent connections. The architecture of LSTM has special memory cells and gating mechanisms that enable the model to capture and retain long-term dependencies. LSTM components and functions breakdown:
| Component | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Cell | Stores Long-Term Information | The core of the LSTM unit, responsible for maintaining and updating data over long periods. Enables long-term retention of information. |
| Input Gate | Controls Data Retention | Decides how much new information should be added to the memory cell, based on the current input and previous state. |
| Forget Gate | Removes Unnecessary Data | Evaluates stored information and discards irrelevant details by considering the current input and prior hidden state. |
| Output Gate | Manages Information Flow | Regulates the release of data from the memory cell to the next time step or layer, based on the present input and previous hidden state. |
| Cell State | Internal Memory | Represents the memory content of the LSTM, interacting with gates to retain or remove information over time. |
| Hidden State | Final Processed Output | The output of the LSTM at a given time step, carrying refined information to the next layer or time step. Influenced by the cell state and output gate. |
The LSTM technique in RNNs aims to tackle the issue of gradient vanishing through the use of input, forget, and output gates that regulate the information flow via gating mechanisms. Leveraging advanced memory cells and gating mechanisms, LSTM networks exhibit outstanding aptitude for carrying out diverse sequential assignments, encompassing, but not limited to, functions such as language modeling, speech recognition, and time series forecasting.
Sequential Memory
Sequential memory refers to the ability of a model to retain information across a sequence of events or time steps. This concept is crucial in fields like natural language processing, speech recognition, and time-series prediction where context over time is essential.

| Memory Type | Description | Use Cases | Example Architectures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term Memory | Retains only recent information, limited in capturing long-term dependencies. | – Real-time applications – Immediate context processing | – RNNs – Vanilla Neural Networks |
| Long-Term Memory | Retains information for a longer duration, crucial for capturing long-term dependencies. | – Long-term prediction tasks – Complex decision making | – LSTMs – GRUs |
| Working Memory | Temporarily stores intermediate information to manipulate or use later in computations. | – Cognitive tasks – Problem-solving systems | – Hybrid models combining memory mechanisms |
| Episodic Memory | Recalls specific past events or episodes with context for improved decision-making. | – Personalization systems – Contextual search | – Memory Networks – Neural Turing Machines |
| Semantic Memory | Stores general knowledge and concepts, independent of context. | – Knowledge graphs – Question answering systems | – Transformer-based models – BERT, GPT |
| External Memory | Uses external storage to augment internal memory, allowing access to vast information beyond the model’s capacity. | – Large-scale data processing – Complex reasoning tasks | – Neural Turing Machines – Memory-augmented Networks |
Sequential memory plays a critical role in AI models, allowing them to remember past information over time, which enhances their ability to make informed decisions. Various architectures like LSTMs and memory networks leverage different memory types for specialized tasks.

Conclusion – I particularly think that getting to know the types of machine learning algorithms actually helps to see a somewhat clear picture. The answer to the question “What machine learning algorithm should I use?” is always “It depends.” It depends on the size, quality, and nature of the data. Also, what is the objective/motive of data torturing? As more we torture data more useful information comes out. It depends on how the math of the algorithm was translated into instructions for the computer you are using. In short, understanding the nuances of various algorithms enables better decision-making in selecting the most suitable approach for a given task.
—
Points to Note:
All credits if any remain on the original contributor only. We have covered all basics around Recurrent Neural Networks. RNNs are all about modelling units in sequence. The perfect support for Natural Language Processing – NLP tasks. Though often such tasks struggle to find the best companion between CNN’s and RNNs’ algorithms to look for information.
Books + Other readings Referred
- Research through open internet, news portals, white papers and imparted knowledge via live conferences & lectures.
- Lab and hands-on experience of @AILabPage (Self-taught learners group) members.
- This useful pdf on NLP parsing with Recursive NN.
- Amazing information in this pdf as well.
Feedback & Further Question
Do you have any questions about Deep Learning or Machine Learning? Leave a comment or ask your question via email. Will try my best to answer it.
======================= About the Author =======================
Read about Author at : About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your opinion / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter
============================================================

[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
I want to say thanks to you. I have bookmark your site for future updates. ExcelR Data Scientist Course Pune
[…] Convolutional Neural Networks applications solve many unsolved problems that could remain unsolved without convolutional neural networks with many layers, include high calibres AI systems such as AI-based robots, virtual assistants, and self-driving cars. Other common applications where CNNs are used as mentioned above like emotion recognition and estimating age/gender etc The best-known models are convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks […]
[…] There are some specialized versions also available. Such as convolution neural networks and recurrent neural networks. These addresses special problem domains. Two of the best use cases for Deep Learning which are […]
[…] https://vinodsblog.com/2019/01/07/deep-learning-introduction-to-recurrent-neural-networks/ […]
Very interesting to read this article.I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. This article inspired me to read more. keep it up.
Correlation vs Covariance
Simple linear regression
data science interview questions
Very interesting to read this article.I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. This article inspired me to read more. keep it up.
Correlation vs Covariance
Simple linear regression
data science interview questions
Amazing Article ! I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. This article inspired me to read more. keep it up.
Simple Linear Regression
Correlation vs covariance
data science interview questions
KNN Algorithm
very well explained .I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. This article inspired me to read more. keep it up.
Simple Linear Regression
Correlation vs covariance
data science interview questions
KNN Algorithm
Logistic Regression explained
This Was An Amazing ! I Haven’t Seen This Type of Blog Ever ! Thankyou For Sharing, data science course in hyderabad with placements
[…] Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks […]
Such a very useful information!Thanks for sharing this useful information with us. Really great effort.
data scientist courses aurangabad
Informative blog
Data science course in pune
Amazing Article! I would like to thank you for the efforts you had made for writing this awesome article. This article inspired me to read more. keep it up.
Data science course in pune
Very informative message! There is so much information here that can help any business start a successful social media campaign!
With the advancement in technology, users are now expecting a web app.
data science course in pondicherry
Thanks for sharing good information I read this post I really like this article.
artificial intelligence training in Hyderabad
In this article, you will read the basic details of both of these languages, and then it will be easy for you to make a decision that is R is easier to learn than Python.data science course in jalandhar
Get dual certification from IBM and UTM, Malaysia with a single Data Science Course at 360DigiTMG. Enroll now for a successful tomorrow!
data science course fees in hyderabad
When one thinks about data science, there might be word machine learning comes into the mind.data science course in nashik
This is additionally a generally excellent post which I truly delighted in perusing.
It isn’t each day that I have the likelihood to see something like this..
data science course in pune
360DigiTMG provides exceptional training in the Data Science course with placements. Learn the strategies and techniques from the best industry experts and kick start your career.data analytics course in jalandhar
All things considered I read it yesterday yet I had a few musings about it and today I needed to peruse it
again in light of the fact that it is very elegantly composed.
full stack data scientist course in Malaysia
I am searching for and I love to post a remark that “The substance of your post is wonderful” Great work!
data analytics course in pune
Python is more popular than R, which is why most organizations use it. R’s functionality is beneficial. That is why the companies prefer it for the beginning of their projects.data science training in dombivli
This post is very simple to read and appreciate without leaving any details out. Great work!data science course in chennai
This is the first time I visit here. I found such a large number of engaging stuff in your blog, particularly its conversation. From the huge amounts of remarks on your articles,
I surmise I am by all accounts not the only one having all the recreation here! Keep doing awesome.
I have been important to compose something like this on my site and you have given me a thought.
Cool you write, the information is very good and interesting, I’ll give you a link to my site.
data analytics course in Hyderabad.
Hi, I have read a lot from this blog thank you for sharing this information. We provide all the essential topics in Data Science Course In Chennai like, Full stack Developer, Python, AI and Machine Learning, Tableau, etc. for more information just log in to our website
Data science course in chennai
Hi, I have read a lot from this blog thank you for sharing this information. We provide all the essential topics in Data Science Course In Dehradun like, Full stack Developer, Python, AI and Machine Learning, Tableau, etc. for more information just log in to our website
Data science course in Dehradun
Hi, I have read a lot from this blog thank you for sharing this information. We provide all the essential topics in Data Science Course In Bhopal like, Full stack Developer, Python, AI and Machine Learning, Tableau, etc. for more information just log in to our website
Data science course in bhopal
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
If you want to know more about data science, certification courses available in this field and placement opportunities upon completion of the courses, this post is the right place to be. It takes you through all of 360digiTMG’s courses in detail and guides you to pick the one that is most suitable for you.data science training certification in hyderabad
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
[…] recurrent neural networks models comes very handy to translate language. Through interactive exercises and using […]
[…] Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks […]
[…] Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks […]
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
I recommend everyone to read this blog, as it contains some of the best ever content you will find on data science. The best part is that the writer has presented the information in an attractive and engaging manner. Every line gives you something new to learn, and this itself tells volumes about the quality of the information presented here.
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) – A neural network to understand the context in speech, text or music. The RNN allows information to loop through the network, […]
[…] Recurrent Unit – The GRU is a variant of the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) architecture designed to overcome the challenges posed by the vanishing gradient […]
[…] in the past, certain deep learning architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), have taken precedence over others because of their effectiveness in various applications, as […]
I enjoyed reading about the latest trends and advancements in the field of data science in this post.
data science institutes in hyderabad
[…] Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks […]
This captivating blog on “Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks” is a commendable exploration of a complex topic, offering clarity and depth to readers. The author’s ability to demystify recurrent neural networks showcases a rare talent for making intricate concepts accessible and engaging. The insightful analysis and clear explanations make this blog an invaluable resource for anyone diving into the world of deep learning.
I appreciate you offering such lovely items. I learned something from your blog. Continue sharing. Your insightful blog post on ‘Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks’ expertly navigates the complexities of this cutting-edge technology, providing a clear and engaging entry point for both novices and seasoned enthusiasts. Your ability to distil intricate concepts into digestible insights truly makes this a valuable resource for anyone delving into the world of deep learning.
I want to say thanks to you. I have bookmark your site for future updates. Ataşehir Çekici
“Deep Learning – Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks” offers a compelling journey into the intricate world of neural networks, specifically focusing on the versatile domain of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). The content provides a clear and insightful introduction, unravelling the complexities of RNNs with clarity and precision. It adeptly navigates through the foundational concepts, making this advanced topic accessible to learners at all levels.
The appreciation extends to the seamless blend of theoretical insights and practical applications, fostering a comprehensive understanding. Overall, this resource stands as an invaluable guide, bridging the gap between theory and implementation in the realm of deep learning.
In short, I enjoyed reading about the latest trends and advancements in the field of Recurrent Neural Networks in this post.
Thank you for sharing this information. I wanted to mention that I’ve visited your website and found it to be both intriguing and informative. I’m looking forward to exploring more of your posts. Allow me to share link for my personal promotion here. Data Science Course in Chennai
The explanation is very clear, and the presentation is neat. Thank you for sharing this article. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a type of artificial neural network designed to process sequences of data. They work especially well for jobs requiring sequences, such as time series data, voice, natural language, and other activities. RNN works on the principle of saving the output of a particular layer and feeding this back to the input in order to predict the output of the layer. please allow me to promote my company, Have a look at our training
Artificial Intelligence Course in Mumbai
Thank you for publishing this blog. RNNs are a type of neural network that can be used to model sequence data. RNNs, which are formed from feedforward networks, are similar to human brains in their behaviour. Simply said, recurrent neural networks can anticipate sequential data in a way that other algorithms can’t.
Excellent post! The information provided is wonderful and incredibly useful. Thank you for sharing and please continue to update. Please allow me to promote my company courses on your site. Thank you once again
Data Science Course in Chennai
Really Enjoyed.
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks […]
Fantastic! You’ve provided clear explanations. It’s very helpful for me to learn about new things. Please allow me to promote my stuff
[…] information for long-term storage. LSTMs includes a distinctive design methodology used for recurrent neural networks (RNNs) with the objective of surmounting the limitations of conventional RNNs in identifying complex […]
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Recursive Neural Networks (ReNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) can be considered as part of the broader family of neural network architectures designed for handling sequential data. […]
thanks for valuable info
gcp training in hyderabad
This is truly informative. Your insights are particularly on point. Thanks for sharing your expertise.
[…] there are recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and their cool cousins, LSTMs and GRUs, which are like storytellers, crafting stories or songs that […]
The Data Science course in Pune, offered by UV Technocrats, is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the core concepts and practical applications of data science. This course covers a wide range of topics, including data analysis, machine learning, statistical modeling, data visualization, and big data technologies. With a focus on hands-on training, students work on real-world projects, gaining the skills needed to analyze complex datasets and make data-driven decisions. UV Technocrats, known for its expert instructors and industry-relevant curriculum, ensures that students are well-equipped to succeed in the competitive field of data science. The course is ideal for professionals and fresh graduates looking to build a solid foundation in data science and advance their careers in this rapidly growing field.
Free Promotion —-
https://www.uvtechnocrats.com/data-science-course-in-pune/
[…] Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) […]
Insightful and well-structured post! I really appreciated how you broke down the concept of recurrent neural networks—especially your explanation of how they handle temporal dependencies in data, and the step-by-step walkthrough of training with sequences. The examples with [e.g., text prediction or time-series data] made the theory feel practical and relevant. I’d love to see a follow-up exploring LSTMs or GRUs in action with code snippets. Keep up the excellent work—this is one of the clearest intros to RNNs I’ve read recently!